Come usare il plugin
Il plugin Runtime Text To Speech sintetizza il testo in voce utilizzando modelli vocali scaricabili. Questi modelli vengono gestiti nelle impostazioni del plugin all'interno dell'editor, scaricati e impacchettati per l'uso a runtime. Segui i passaggi qui sotto per iniziare.
Lato editor
Scarica i modelli vocali appropriati per il tuo progetto come descritto qui. Puoi scaricare più modelli vocali contemporaneamente.
Lato runtime
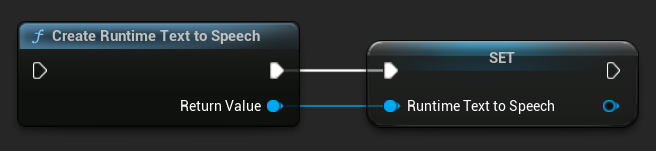
Crea il sintetizzatore utilizzando la funzione CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech. Assicurati di mantenere un riferimento ad esso (ad esempio come variabile separata in Blueprints o UPROPERTY in C++) per evitare che venga eliminato dal garbage collector.
- Blueprint
- C++
// Create the Runtime Text To Speech synthesizer in C++
URuntimeTextToSpeech* Synthesizer = URuntimeTextToSpeech::CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech();
// Ensure the synthesizer is referenced correctly to prevent garbage collection (e.g. as a UPROPERTY)
Sintesi Vocale
Il plugin offre due modalità di sintesi vocale da testo:
- Sintesi Vocale Regolare: Sintetizza l'intero testo e restituisce l'audio completo al termine
- Sintesi Vocale in Streaming: Fornisce frammenti audio man mano che vengono generati, consentendo un'elaborazione in tempo reale
Ogni modalità supporta due metodi per selezionare i modelli vocali:
- Per Nome: Seleziona un modello vocale tramite il suo nome (consigliato per UE 5.4+)
- Per Oggetto: Seleziona un modello vocale tramite riferimento diretto (consigliato per UE 5.3 e versioni precedenti)
Sintesi Vocale Regolare
Per Nome
- Blueprint
- C++
La funzione Text To Speech (By Name) è più comoda negli Blueprints a partire da UE 5.4. Ti consente di selezionare i modelli vocali da un menu a tendina dei modelli scaricati. Nelle versioni UE inferiori alla 5.3, questo menu a tendina non appare, quindi se stai utilizzando una versione precedente, dovrai scorrere manualmente l'array dei modelli vocali restituito da GetDownloadedVoiceModels per selezionare quello necessario.
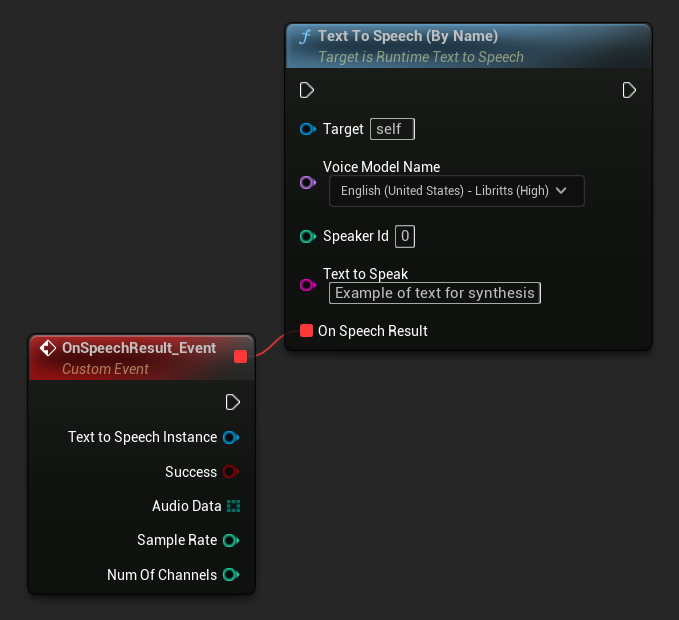
In C++, la selezione dei modelli vocali può essere leggermente più complessa a causa della mancanza di un menu a tendina. Puoi utilizzare la funzione GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames per recuperare i nomi dei modelli vocali scaricati e selezionare quello necessario. Successivamente, puoi chiamare la funzione TextToSpeechByName per sintetizzare il testo utilizzando il nome del modello vocale selezionato.
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, just as an example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumChannels)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("TextToSpeech result: %s, AudioData size: %d, SampleRate: %d, NumChannels: %d"), bSuccess ? TEXT("Success") : TEXT("Failed"), AudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumChannels);
}));
return;
}
Per Oggetto
- Blueprint
- C++
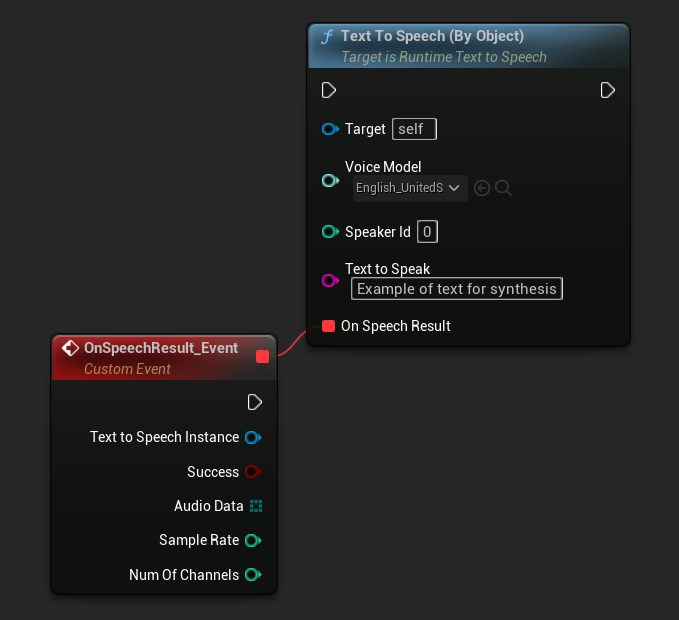
La funzione Text To Speech (By Object) funziona su tutte le versioni di Unreal Engine ma presenta i modelli vocali come un elenco a discesa di riferimenti agli asset, il che è meno intuitivo. Questo metodo è adatto per UE 5.3 e versioni precedenti, o se il tuo progetto richiede un riferimento diretto a un asset del modello vocale per qualsiasi motivo.
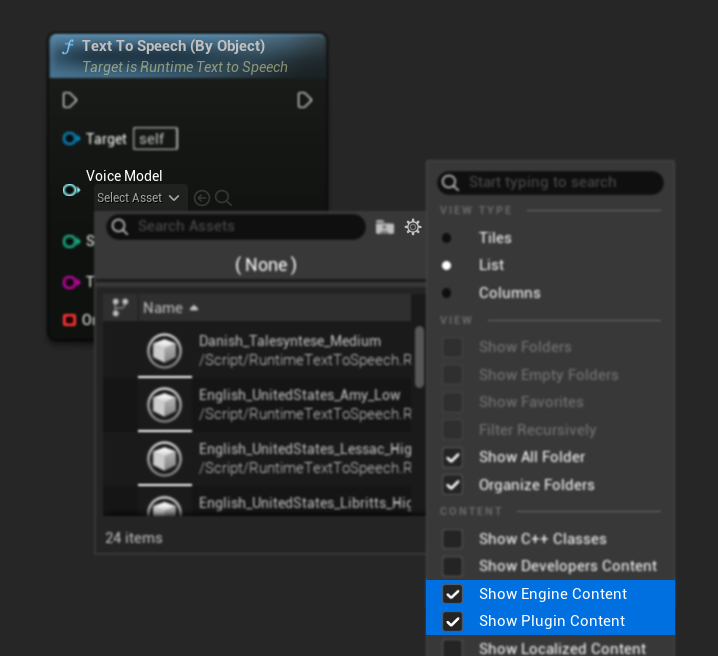
Se hai scaricato i modelli ma non riesci a vederli, apri il menu a discesa Voice Model, clicca sulle impostazioni (icona dell'ingranaggio) e abilita sia Mostra Contenuti Plugin che Mostra Contenuti Engine per rendere visibili i modelli.
In C++, la selezione dei modelli vocali può essere leggermente più complessa a causa della mancanza di un elenco a discesa. Puoi utilizzare la funzione GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames per recuperare i nomi dei modelli vocali scaricati e selezionare quello di cui hai bisogno. Successivamente, puoi chiamare la funzione GetVoiceModelFromName per ottenere l'oggetto del modello vocale e passarlo alla funzione TextToSpeechByObject per sintetizzare il testo.
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
TSoftObjectPtr<URuntimeTTSModel> VoiceModel;
if (!URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetVoiceModelFromName(VoiceName, VoiceModel))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to get voice model from name: %s"), *VoiceName.ToString());
return;
}
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByObject(VoiceModel, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumChannels)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("TextToSpeech result: %s, AudioData size: %d, SampleRate: %d, NumChannels: %d"), bSuccess ? TEXT("Success") : TEXT("Failed"), AudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumChannels);
}));
return;
}
Sintesi Vocale in Streaming
Per testi più lunghi o quando si desidera elaborare i dati audio in tempo reale man mano che vengono generati, è possibile utilizzare le versioni in streaming delle funzioni di Sintesi Vocale:
Streaming Text To Speech (By Name)(StreamingTextToSpeechByNamein C++)Streaming Text To Speech (By Object)(StreamingTextToSpeechByObjectin C++)
Queste funzioni forniscono i dati audio in blocchi man mano che vengono generati, consentendo un'elaborazione immediata senza dover attendere il completamento dell'intera sintesi. Ciò è utile per varie applicazioni come la riproduzione audio in tempo reale, la visualizzazione live o qualsiasi scenario in cui è necessario elaborare i dati vocali in modo incrementale.
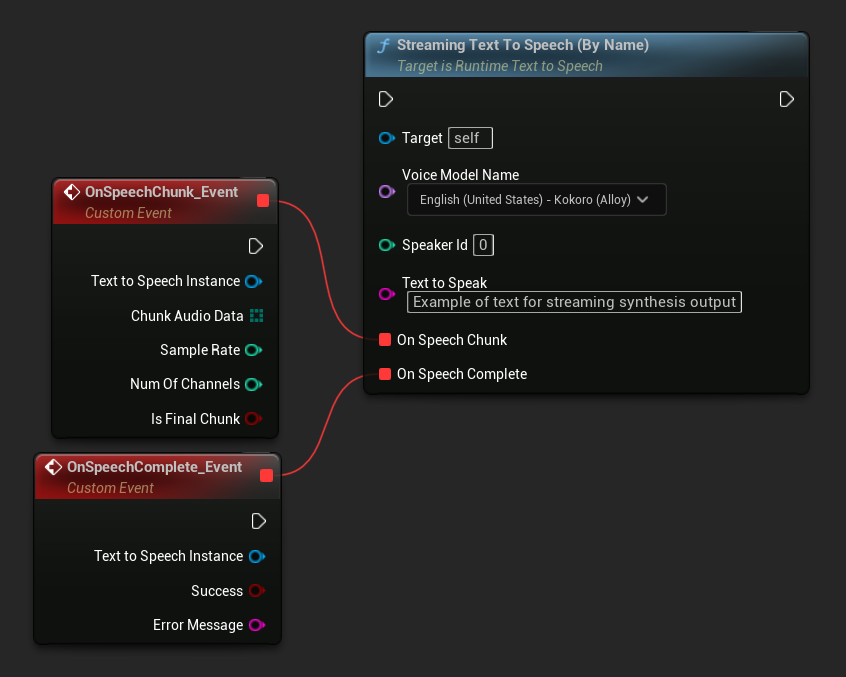
Streaming By Name
- Blueprint
- C++
La funzione Streaming Text To Speech (By Name) funziona in modo simile alla versione regolare ma fornisce l'audio in blocchi attraverso il delegato On Speech Chunk.
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByName(
VoiceName,
0,
TEXT("This is a long text that will be synthesized in chunks."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
// Process each chunk of audio data as it becomes available
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Received chunk %d with %d bytes of audio data. Sample rate: %d, Channels: %d, Is Final: %s"),
ChunkIndex, ChunkAudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumOfChannels, bIsFinalChunk ? TEXT("Yes") : TEXT("No"));
// You can start processing/playing this chunk immediately
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
// Called when the entire synthesis is complete or if it fails
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming synthesis completed successfully"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
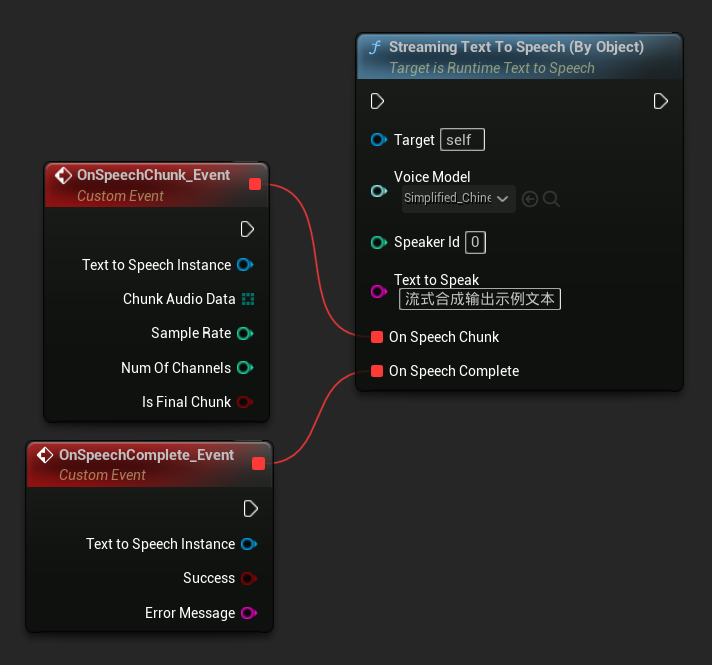
Streaming Per Oggetto
- Blueprint
- C++
La funzione Streaming Text To Speech (By Object) fornisce la stessa funzionalità di streaming ma prende un riferimento all'oggetto modello vocale.
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
TSoftObjectPtr<URuntimeTTSModel> VoiceModel;
if (!URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetVoiceModelFromName(VoiceName, VoiceModel))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to get voice model from name: %s"), *VoiceName.ToString());
return;
}
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByObject(
VoiceModel,
0,
TEXT("This is a long text that will be synthesized in chunks."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
// Process each chunk of audio data as it becomes available
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Received chunk %d with %d bytes of audio data. Sample rate: %d, Channels: %d, Is Final: %s"),
ChunkIndex, ChunkAudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumOfChannels, bIsFinalChunk ? TEXT("Yes") : TEXT("No"));
// You can start processing/playing this chunk immediately
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
// Called when the entire synthesis is complete or if it fails
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming synthesis completed successfully"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
Riproduzione Audio
- Riproduzione Regolare
- Streaming Playback
Per il text-to-speech regolare (non in streaming), il delegato On Speech Result fornisce l'audio sintetizzato come dati PCM in formato float (come un array di byte in Blueprints o TArray<uint8> in C++), insieme al Sample Rate e al Num Of Channels.
Per la riproduzione, si consiglia di utilizzare il plugin Runtime Audio Importer per convertire i dati audio grezzi in un'onda sonora riproducibile.
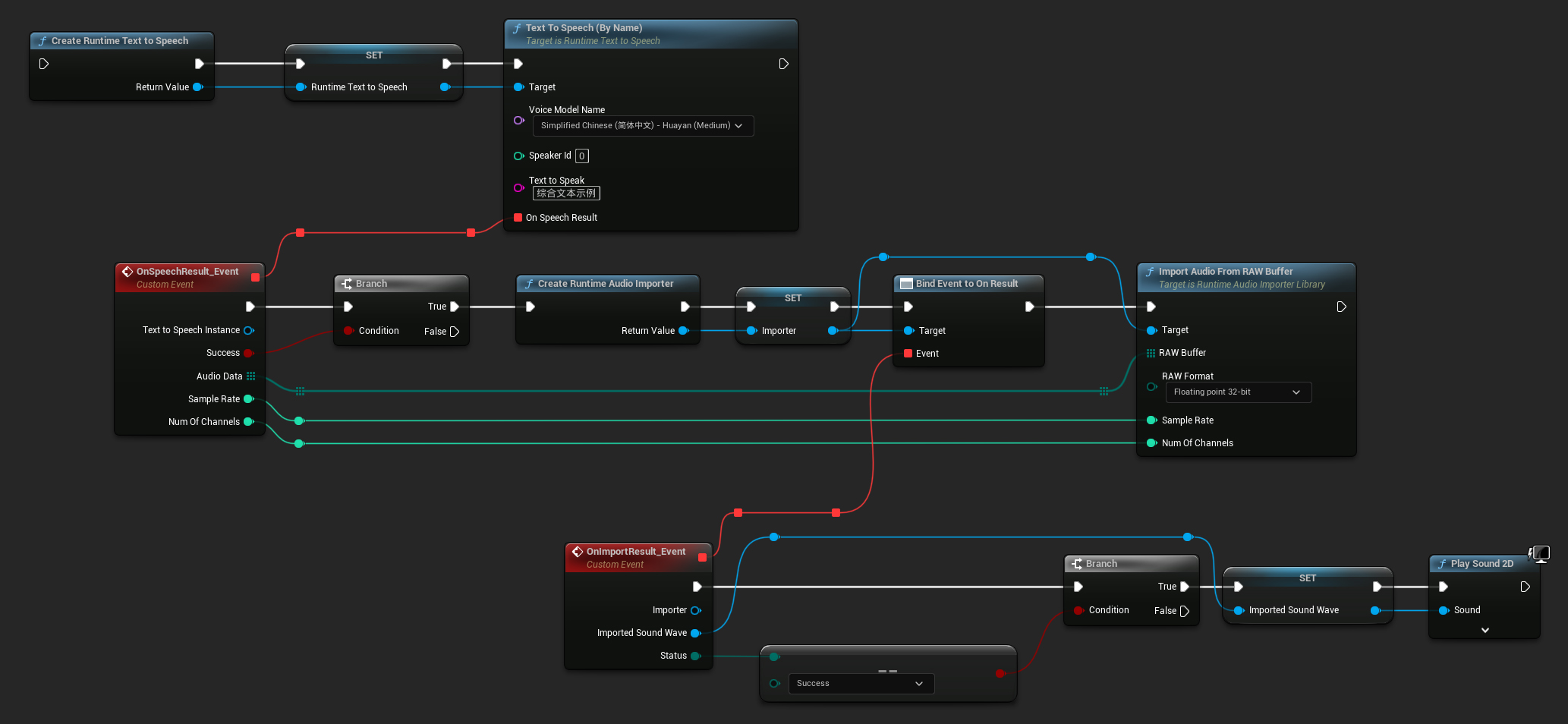
- Blueprint
- C++
Ecco un esempio di come potrebbero apparire i nodi Blueprint per sintetizzare il testo e riprodurre l'audio (Nodi copiabili):
Ecco un esempio di come sintetizzare il testo e riprodurre l'audio in C++:
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
// Ensure "this" is a valid and referenced UObject (must not be eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels)
{
if (!bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("TextToSpeech failed"));
return;
}
// Create the Runtime Audio Importer to process the audio data
URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* RuntimeAudioImporter = URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary::CreateRuntimeAudioImporter();
// Prevent the RuntimeAudioImporter from being garbage collected by adding it to the root (you can also use a UPROPERTY, TStrongObjectPtr, etc.)
RuntimeAudioImporter->AddToRoot();
RuntimeAudioImporter->OnResultNative.AddWeakLambda(RuntimeAudioImporter, [this](URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* Importer, UImportedSoundWave* ImportedSoundWave, ERuntimeImportStatus Status)
{
// Once done, remove it from the root to allow garbage collection
Importer->RemoveFromRoot();
if (Status != ERuntimeImportStatus::SuccessfulImport)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to import audio, status: %s"), *UEnum::GetValueAsString(Status));
return;
}
// Play the imported sound wave (ensure a reference is kept to prevent garbage collection)
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), ImportedSoundWave);
});
RuntimeAudioImporter->ImportAudioFromRAWBuffer(AudioData, ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Float32, SampleRate, NumOfChannels);
}));
return;
}
Per lo streaming di text-to-speech, riceverai i dati audio in blocchi come dati PCM in formato float (come un array di byte in Blueprints o TArray<uint8> in C++), insieme a Sample Rate e Num Of Channels. Ogni blocco può essere elaborato immediatamente non appena diventa disponibile.
Per la riproduzione in tempo reale, si consiglia di utilizzare il plugin Runtime Audio Importer Streaming Sound Wave, che è specificamente progettato per la riproduzione audio in streaming o l'elaborazione in tempo reale.
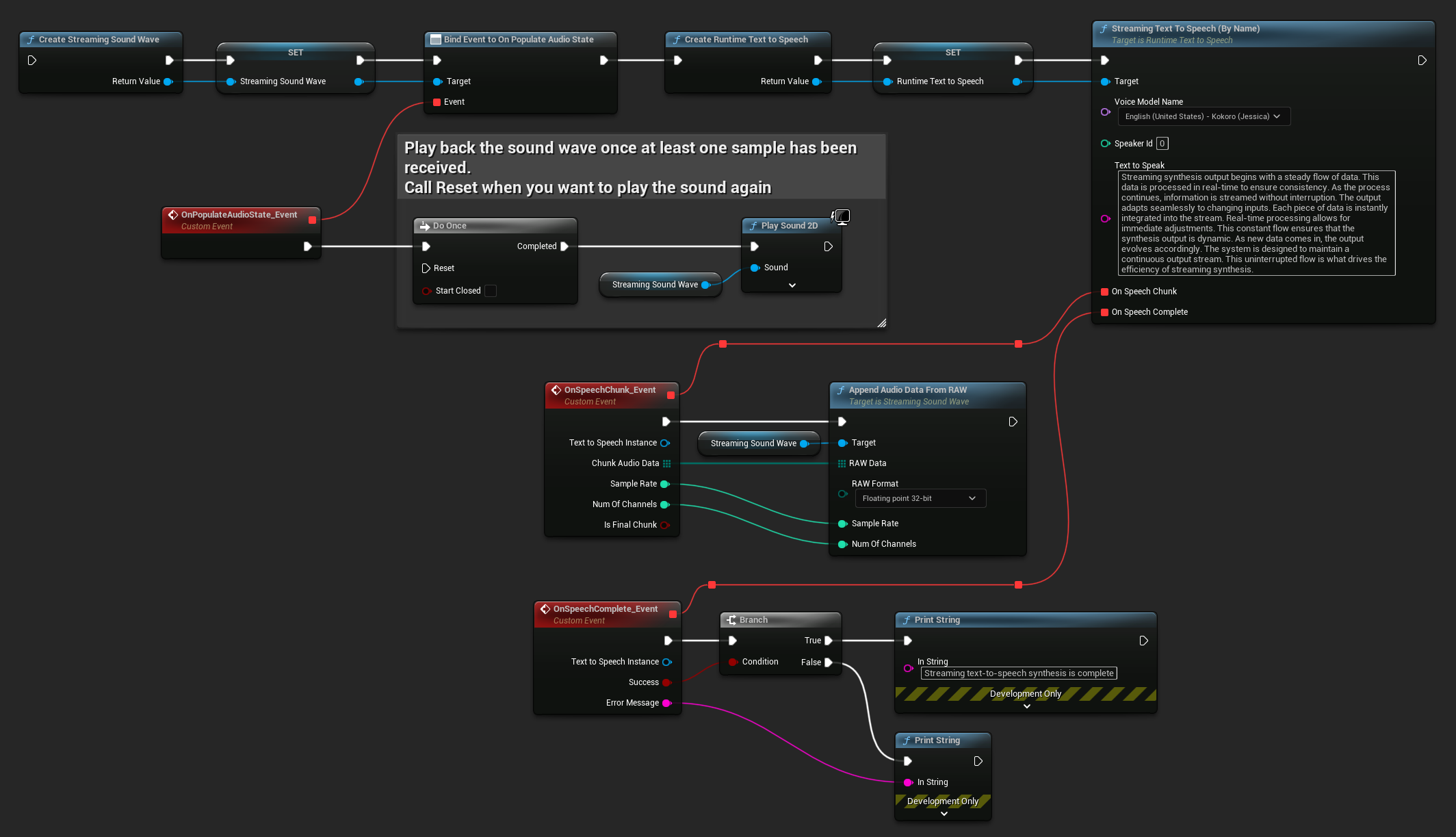
- Blueprint
- C++
Ecco un esempio di come potrebbero apparire i nodi Blueprint per lo streaming di text-to-speech e la riproduzione dell'audio (Nodi copiabili):
Ecco un esempio di come implementare lo streaming di text-to-speech con riproduzione in tempo reale in C++:
UPROPERTY()
URuntimeTextToSpeech* Synthesizer;
UPROPERTY()
UStreamingSoundWave* StreamingSoundWave;
UPROPERTY()
bool bIsPlaying = false;
void StartStreamingTTS()
{
// Create synthesizer if not already created
if (!Synthesizer)
{
Synthesizer = URuntimeTextToSpeech::CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech();
}
// Create a sound wave for streaming if not already created
if (!StreamingSoundWave)
{
StreamingSoundWave = UStreamingSoundWave::CreateStreamingSoundWave();
StreamingSoundWave->OnPopulateAudioStateNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [this]()
{
if (!bIsPlaying)
{
bIsPlaying = true;
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), StreamingSoundWave);
}
});
}
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByName(
VoiceName,
0,
TEXT("Streaming synthesis output begins with a steady flow of data. This data is processed in real-time to ensure consistency. As the process continues, information is streamed without interruption. The output adapts seamlessly to changing inputs. Each piece of data is instantly integrated into the stream. Real-time processing allows for immediate adjustments. This constant flow ensures that the synthesis output is dynamic. As new data comes in, the output evolves accordingly. The system is designed to maintain a continuous output stream. This uninterrupted flow is what drives the efficiency of streaming synthesis."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
StreamingSoundWave->AppendAudioDataFromRAW(ChunkAudioData, ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Float32, SampleRate, NumOfChannels);
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming text-to-speech synthesis is complete"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
}
Annullamento del Text-to-Speech
Puoi annullare un'operazione di sintesi vocale in corso in qualsiasi momento chiamando la funzione CancelSpeechSynthesis sulla tua istanza del sintetizzatore:
- Blueprint
- C++
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid URuntimeTextToSpeech instance
// Start a long synthesis operation
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Very long text..."), ...);
// Later, if you need to cancel it:
bool bWasCancelled = Synthesizer->CancelSpeechSynthesis();
if (bWasCancelled)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Successfully cancelled ongoing synthesis"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("No synthesis was in progress to cancel"));
}
Quando una sintesi viene annullata:
- Il processo di sintesi si interromperà il prima possibile
- Qualsiasi callback in corso verrà terminata
- Il delegato di completamento verrà chiamato con
bSuccess = falsee un messaggio di errore che indica che la sintesi è stata annullata - Qualsiasi risorsa allocata per la sintesi verrà adeguatamente ripulita
Questo è particolarmente utile per testi lunghi o quando è necessario interrompere la riproduzione per avviare una nuova sintesi.
Selezione del Parlante
Entrambe le funzioni Text To Speech accettano un parametro opzionale ID parlante, che è utile quando si lavora con modelli vocali che supportano più parlanti. Puoi utilizzare le funzioni GetSpeakerCountFromVoiceModel o GetSpeakerCountFromModelName per verificare se il modello vocale scelto supporta più parlanti. Se sono disponibili più parlanti, specifica semplicemente l'ID del parlante desiderato quando chiami le funzioni Text To Speech. Alcuni modelli vocali offrono un'ampia varietà - ad esempio, English LibriTTS include oltre 900 parlanti diversi tra cui scegliere.
Il plugin Runtime Audio Importer fornisce anche funzionalità aggiuntive come l'esportazione dei dati audio in un file, il passaggio a SoundCue, MetaSound e altro ancora. Per ulteriori dettagli, consulta la documentazione di Runtime Audio Importer.