Captura de Áudio do Pixel Streaming
Pixel Streaming é um plugin para Unreal Engine que transmite quadros renderizados e sincroniza entrada/saída via WebRTC. A aplicação é executada no lado do servidor, enquanto o lado do cliente lida com a renderização e interação do usuário. Para mais detalhes sobre Pixel Streaming e configuração, consulte a Documentação do Pixel Streaming.
Pixel Streaming vs Pixel Streaming 2
Este plugin suporta ambas as versões do Pixel Streaming disponíveis no Unreal Engine:
- Pixel Streaming - O plugin original, disponível desde o UE 5.2 e ainda ativamente usado nas versões atuais do motor
- Pixel Streaming 2 - Introduzido no UE 5.5 como uma implementação de próxima geração com uma arquitetura interna aprimorada. Saiba mais sobre o Pixel Streaming 2
Ambas as versões são totalmente suportadas e disponíveis nas versões mais recentes do Unreal Engine. Escolha a versão que corresponde à configuração do Pixel Streaming do seu projeto.
A API para ambas as versões é idêntica, com a única diferença sendo que as classes e funções do Pixel Streaming 2 incluem "2" em seus nomes (por exemplo, UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave vs UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave).
Compatibilidade
Esta solução funciona com:
- Infraestrutura oficial do Pixel Streaming (implementação de referência da Epic Games)
- Provedores de Pixel Streaming de terceiros incluindo:
- Vagon.io
- Arcane Mirage
- Eagle 3D Streaming
- Outras soluções de streaming baseadas em WebRTC
- Sistemas operacionais: Servidores Windows e Linux
A implementação foi testada nestes ambientes e funciona corretamente independentemente da solução de hospedagem do Pixel Streaming utilizada.
Instalação do Plugin de Extensão
Este recurso é fornecido como uma extensão para o plugin Runtime Audio Importer. Para usá-lo, você precisa:
- Certificar-se de que o plugin Runtime Audio Importer já está instalado em seu projeto
- Baixar o plugin de extensão para sua versão do Pixel Streaming:
- Extrair a pasta do arquivo baixado para a pasta
Pluginsdo seu projeto (crie esta pasta se ela não existir) - Recompilar seu projeto (esta extensão requer um projeto C++)
- Estas extensões são fornecidas como código-fonte e requerem um projeto C++ para uso
- Extensão Pixel Streaming: Suportada no UE 5.2 e posterior
- Extensão Pixel Streaming 2: Suportada no UE 5.5 e posterior
- Para mais informações sobre como construir plugins manualmente, veja o tutorial Construindo Plugins
Visão Geral
A Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming estende a Onda Sonora Capturável padrão para permitir a captura de áudio diretamente dos microfones dos clientes do Pixel Streaming. Este recurso permite que você:
- Capture áudio de navegadores conectados via Pixel Streaming
- Processe áudio de jogadores/pares específicos
- Implemente chat de voz, comandos de voz ou gravação de áudio de usuários remotos
Uso Básico
Criando uma Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming
Primeiro, você precisa criar um objeto de Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming:
- Pixel Streaming
- Pixel Streaming 2
- Blueprint
- C++
![]()
PixelStreamingSoundWave = UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave::CreatePixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave();
- Blueprint
- C++
Use o nó Create Pixel Streaming 2 Capturable Sound Wave (o mesmo que Pixel Streaming, mas com "2" no nome)
PixelStreamingSoundWave = UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave::CreatePixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave();
Você deve tratar o Pixel Streaming Capturable Sound Wave como uma referência forte para evitar sua destruição prematura (por exemplo, atribuindo-a a uma variável separada em Blueprints ou usando UPROPERTY() em C++).
Iniciando e Parando a Captura
Você pode iniciar e parar a captura de áudio com chamadas de função simples:
- Pixel Streaming
- Pixel Streaming 2
- Blueprint
- C++
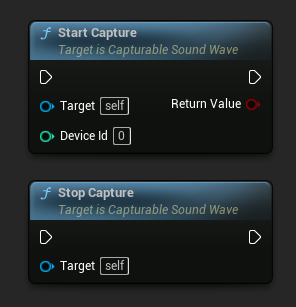
// Assuming PixelStreamingSoundWave is a reference to a UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave object
// Start capturing audio (the device ID parameter is ignored for Pixel Streaming)
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StartCapture(0);
// Stop capturing audio
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StopCapture();
- Blueprint
- C++
Use os mesmos nós Start Capture e Stop Capture com sua Capturable Sound Wave do Pixel Streaming 2
// Assuming PixelStreamingSoundWave is a reference to a UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave object
// Start capturing audio (the device ID parameter is ignored for Pixel Streaming 2)
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StartCapture(0);
// Stop capturing audio
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StopCapture();
O parâmetro DeviceId em StartCapture é ignorado para Pixel Streaming Capturable Sound Waves, pois a fonte de captura é determinada automaticamente ou pelas informações do jogador que você definiu.
Verificando o Status da Captura
Você pode verificar se a onda sonora está atualmente capturando áudio:
- Pixel Streaming
- Pixel Streaming 2
- Blueprint
- C++
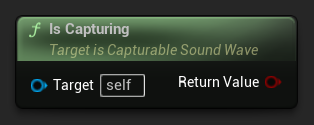
// Assuming PixelStreamingSoundWave is a reference to a UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave object
bool bIsCapturing = PixelStreamingSoundWave->IsCapturing();
- Blueprint
- C++
Use o mesmo nó Is Capturing com sua Capturable Sound Wave do Pixel Streaming 2
// Assuming PixelStreamingSoundWave is a reference to a UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave object
bool bIsCapturing = PixelStreamingSoundWave->IsCapturing();
Exemplo Completo
Aqui está um exemplo completo de como configurar a captura de áudio do Pixel Streaming:
- Pixel Streaming
- Pixel Streaming 2
- Blueprint
- C++
![]()
Este é um exemplo de código básico para capturar dados de áudio de um cliente Pixel Streaming.
O exemplo usa a função CapturePixelStreamingAudioExample localizada na classe UPixelStreamingAudioExample dentro do módulo EXAMPLEMODULE.
Para executar o exemplo com sucesso, certifique-se de adicionar os módulos RuntimeAudioImporter e PixelStreaming tanto a PublicDependencyModuleNames quanto a PrivateDependencyModuleNames no arquivo .Build.cs, bem como ao arquivo .uproject do seu projeto.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "UObject/Object.h"
#include "PixelStreamingAudioExample.generated.h"
UCLASS(BlueprintType)
class EXAMPLEMODULE_API UPixelStreamingAudioExample : public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
void CapturePixelStreamingAudioExample();
private:
// Keep a strong reference to prevent garbage collection
UPROPERTY()
class UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave* PixelStreamingSoundWave;
};
#include "PixelStreamingAudioExample.h"
#include "Sound/PixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave.h"
#include "Kismet/GameplayStatics.h"
void UPixelStreamingAudioExample::CapturePixelStreamingAudioExample()
{
// Create a Pixel Streaming Capturable Sound Wave
PixelStreamingSoundWave = UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave::CreatePixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave();
// Start capturing audio
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StartCapture(0);
// Play the sound wave to hear the captured audio
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), PixelStreamingSoundWave);
// Set up a timer to stop capture after 30 seconds (just for demonstration)
FTimerHandle TimerHandle;
GetWorld()->GetTimerManager().SetTimer(TimerHandle, [this]()
{
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StopCapture();
}, 30.0f, false);
}
- Blueprint
- C++
A configuração de Blueprint é idêntica ao Pixel Streaming, mas use o nó Create Pixel Streaming 2 Capturable Sound Wave em vez disso
Este é um exemplo de código básico para capturar dados de áudio de um cliente Pixel Streaming 2.
O exemplo usa a função CapturePixelStreaming2AudioExample localizada na classe UPixelStreaming2AudioExample dentro do módulo EXAMPLEMODULE.
Para executar o exemplo com sucesso, certifique-se de adicionar os módulos RuntimeAudioImporter e PixelStreaming2 tanto a PublicDependencyModuleNames quanto a PrivateDependencyModuleNames no arquivo .Build.cs, bem como ao arquivo .uproject do seu projeto.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "UObject/Object.h"
#include "PixelStreaming2AudioExample.generated.h"
UCLASS(BlueprintType)
class EXAMPLEMODULE_API UPixelStreaming2AudioExample : public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
void CapturePixelStreaming2AudioExample();
private:
// Keep a strong reference to prevent garbage collection
UPROPERTY()
class UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave* PixelStreamingSoundWave;
};
#include "PixelStreaming2AudioExample.h"
#include "Sound/PixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave.h"
#include "Kismet/GameplayStatics.h"
void UPixelStreaming2AudioExample::CapturePixelStreaming2AudioExample()
{
// Create a Pixel Streaming 2 Capturable Sound Wave
PixelStreamingSoundWave = UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave::CreatePixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave();
// Start capturing audio
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StartCapture(0);
// Play the sound wave to hear the captured audio
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), PixelStreamingSoundWave);
// Set up a timer to stop capture after 30 seconds (just for demonstration)
FTimerHandle TimerHandle;
GetWorld()->GetTimerManager().SetTimer(TimerHandle, [this]()
{
PixelStreamingSoundWave->StopCapture();
}, 30.0f, false);
}
Trabalhando com Múltiplos Players de Pixel Streaming
Em cenários onde você tem múltiplos clientes de Pixel Streaming conectados simultaneamente, pode ser necessário capturar áudio de players específicos. Os seguintes recursos ajudam você a gerenciar isso.
Obtendo Players de Pixel Streaming Disponíveis
Para identificar quais players de Pixel Streaming estão conectados:
- Pixel Streaming
- Pixel Streaming 2
- Blueprint
- C++
![]()
UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave::GetAvailablePixelStreamingPlayers(FOnGetAvailablePixelStreamingPlayersResultNative::CreateWeakLambda(this, [](const TArray<FPixelStreamingPlayerInfo_RAI>& AvailablePlayers)
{
// Handle the list of available players
for (const FPixelStreamingPlayerInfo_RAI& PlayerInfo : AvailablePlayers)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Available player: %s on streamer: %s"), *PlayerInfo.PlayerId, *PlayerInfo.StreamerId);
}
}));
- Blueprint
- C++
Use o nó Get Available Pixel Streaming 2 Players
UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave::GetAvailablePixelStreaming2Players(FOnGetAvailablePixelStreaming2PlayersResultNative::CreateWeakLambda(this, [](const TArray<FPixelStreaming2PlayerInfo_RAI>& AvailablePlayers)
{
// Handle the list of available players
for (const FPixelStreaming2PlayerInfo_RAI& PlayerInfo : AvailablePlayers)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Available player: %s on streamer: %s"), *PlayerInfo.PlayerId, *PlayerInfo.StreamerId);
}
}));
Configurando o Jogador para Capturar
Quando você precisa capturar de um jogador específico:
- Pixel Streaming
- Pixel Streaming 2
- Blueprint
- C++
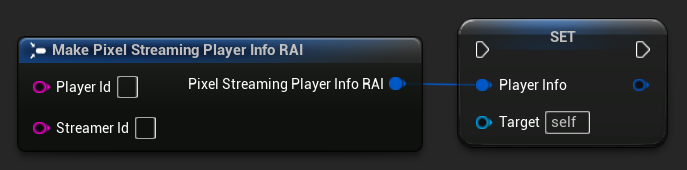
// Assuming PixelStreamingSoundWave is a reference to a UPixelStreamingCapturableSoundWave object
// and PlayerInfo is a FPixelStreamingPlayerInfo_RAI object from GetAvailablePixelStreamingPlayers
PixelStreamingSoundWave->PlayerInfo = PlayerInfo;
- Blueprint
- C++
Use o nó Set Player To Capture From com sua Capturable Sound Wave do Pixel Streaming 2
// Assuming PixelStreamingSoundWave is a reference to a UPixelStreaming2CapturableSoundWave object
// and PlayerInfo is a FPixelStreaming2PlayerInfo_RAI object from GetAvailablePixelStreaming2Players
PixelStreamingSoundWave->PlayerInfo = PlayerInfo;
Se você deixar o ID do Jogador vazio, a onda sonora ouvirá automaticamente o primeiro jogador disponível que se conectar. Este é o comportamento padrão e funciona bem para cenários de jogador único.
Casos de Uso Comuns
Implementação de Chat de Voz
Você pode usar as Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming para implementar chat de voz entre usuários remotos e jogadores locais:
- Crie uma Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming para cada jogador conectado
- Configure um sistema para gerenciar quais jogadores estão falando no momento
- Use o sistema de Detecção de Atividade de Voz para detectar quando os usuários estão falando
- Espacialize o áudio usando o sistema de áudio do Unreal Engine, se necessário
Comandos de Voz com Reconhecimento de Fala
Você pode implementar reconhecimento de comandos de voz para usuários remotos combinando este recurso com o plugin Runtime Speech Recognizer:
- Capture áudio dos clientes do Pixel Streaming usando a Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming
- Alimente o áudio capturado diretamente para o Runtime Speech Recognizer
- Processe o texto reconhecido na lógica do seu jogo
Simplesmente substitua a Onda Sonora Capturável padrão por uma Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming (ou Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming 2) nos exemplos do Runtime Speech Recognizer, e ele funcionará perfeitamente com a entrada de áudio do Pixel Streaming.
Gravação de Áudio de Usuários Remotos
Você pode gravar áudio de usuários remotos para reprodução posterior:
- Capture áudio usando a Onda Sonora Capturável do Pixel Streaming
- Exporte o áudio capturado para um arquivo usando Exportar Áudio
- Salve o arquivo para uso ou análise posterior