Audio Processing Guide
This guide covers how to set up different audio input methods to feed audio data to your lip sync generators. Make sure you've completed the Setup Guide before proceeding.
Audio Input Processing
You need to set up a method to process audio input. There are several ways to do this depending on your audio source.
- Microphone (Real-time)
- Microphone (Playback)
- Text-to-Speech (Local)
- Text-to-Speech (External APIs)
- From Audio File/Buffer
- Streaming Audio Buffer
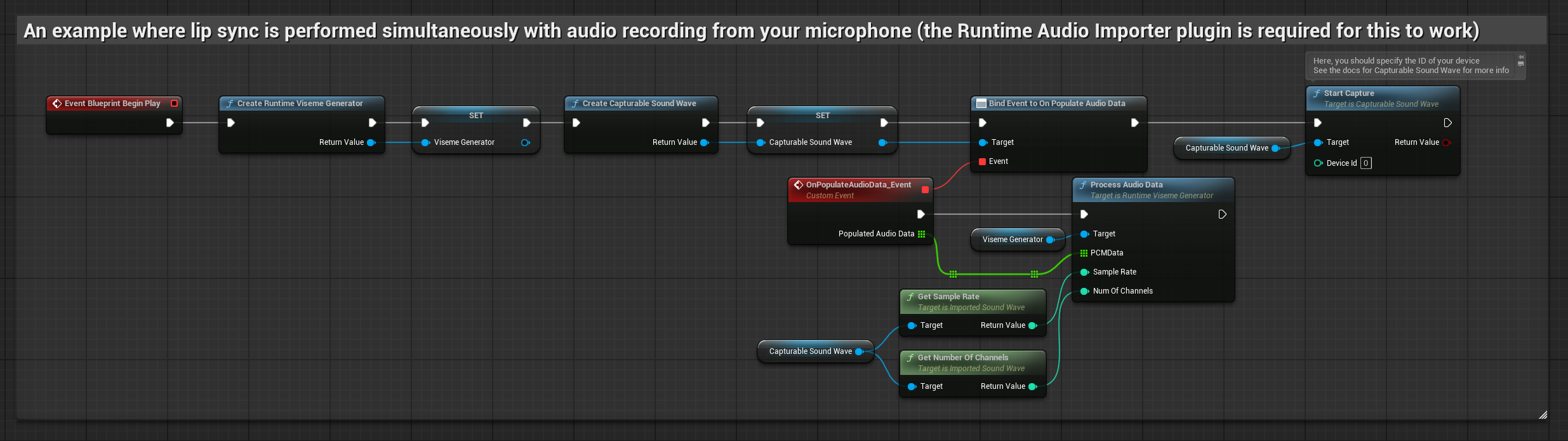
This approach performs lip sync in real-time while speaking into the microphone:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Create a Capturable Sound Wave using Runtime Audio Importer
- For Linux with Pixel Streaming, use Pixel Streaming Capturable Sound Wave instead
- Before starting to capture audio, bind to the
OnPopulateAudioDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator - Start capturing audio from the microphone
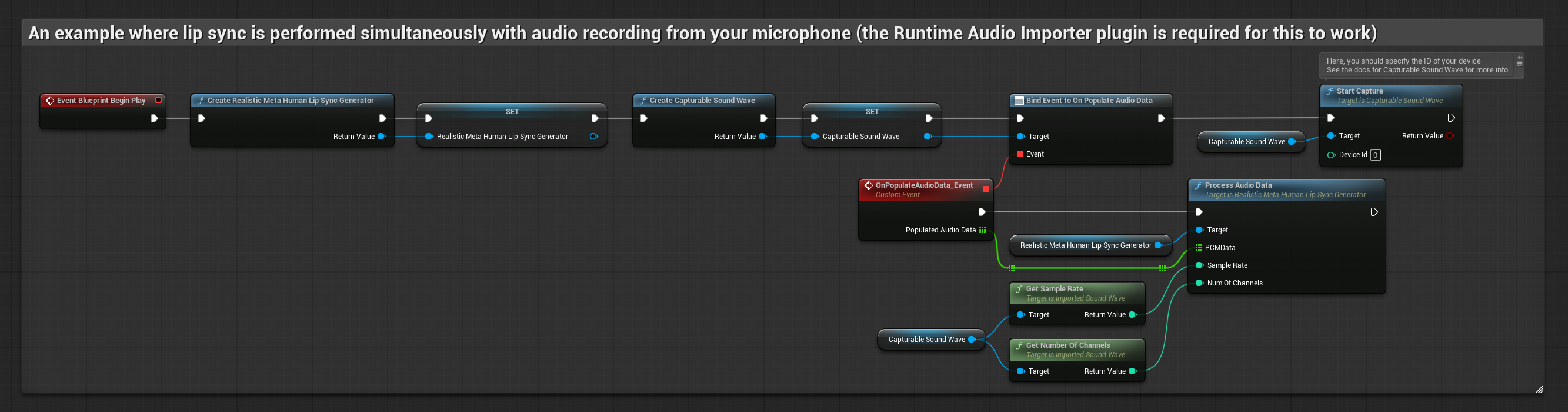
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
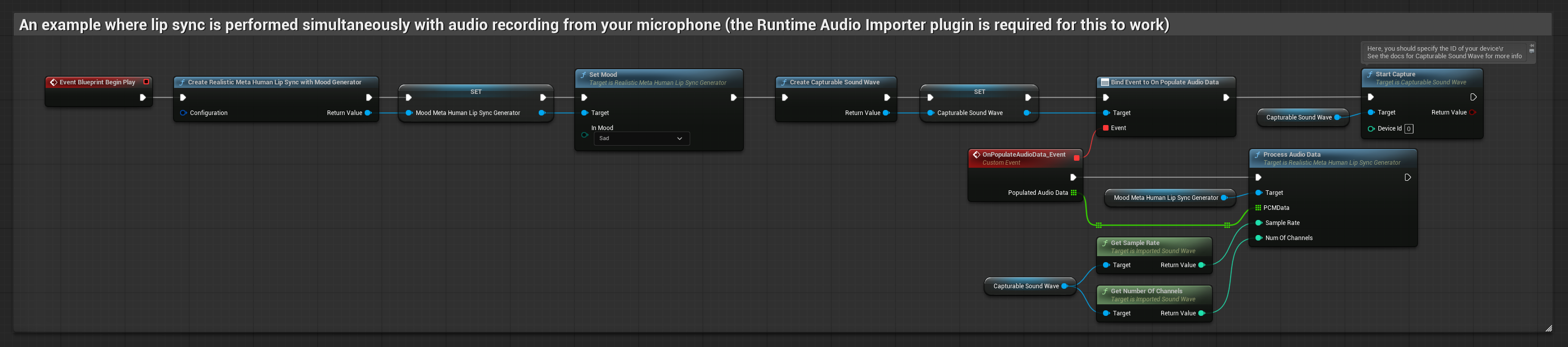
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
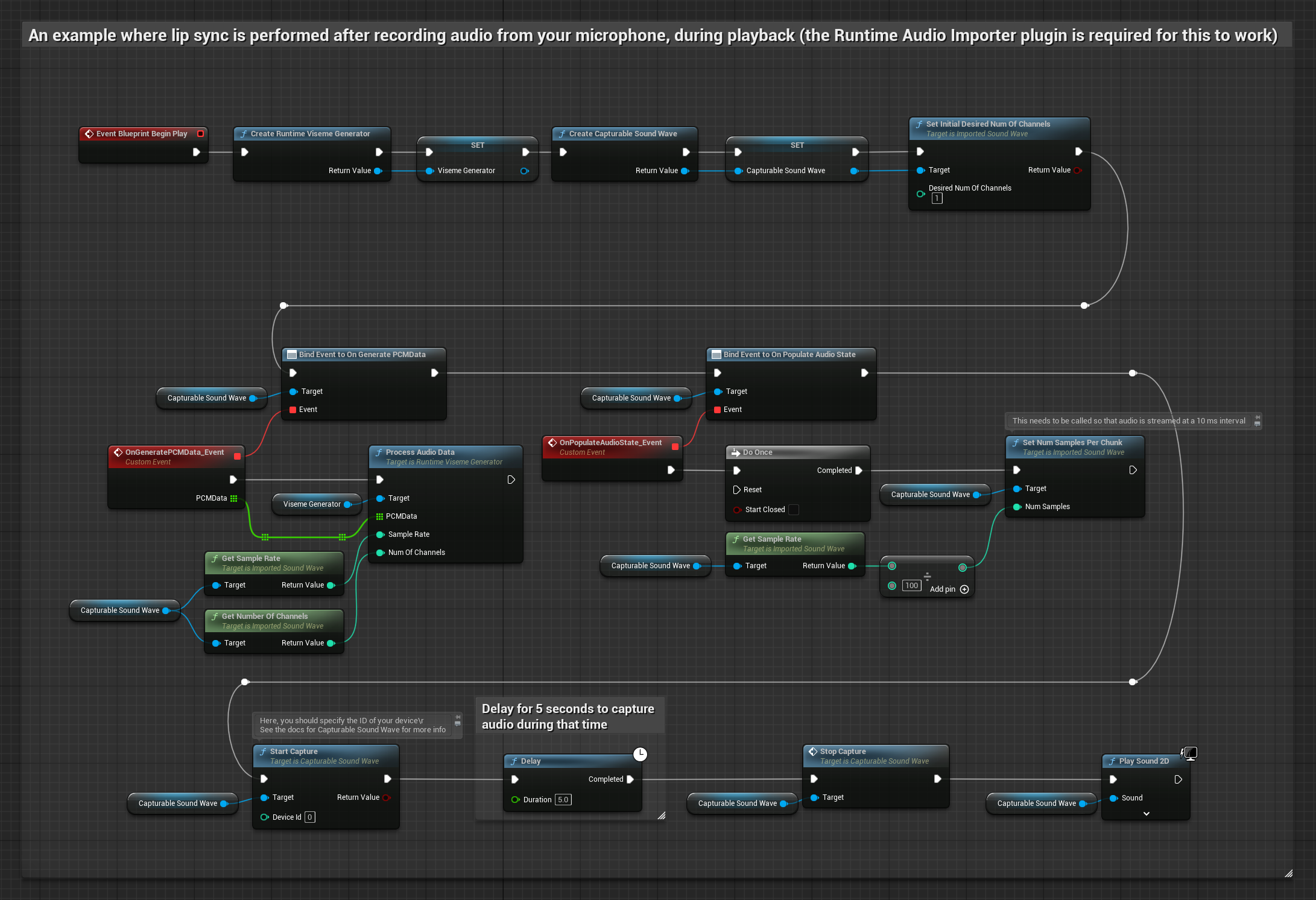
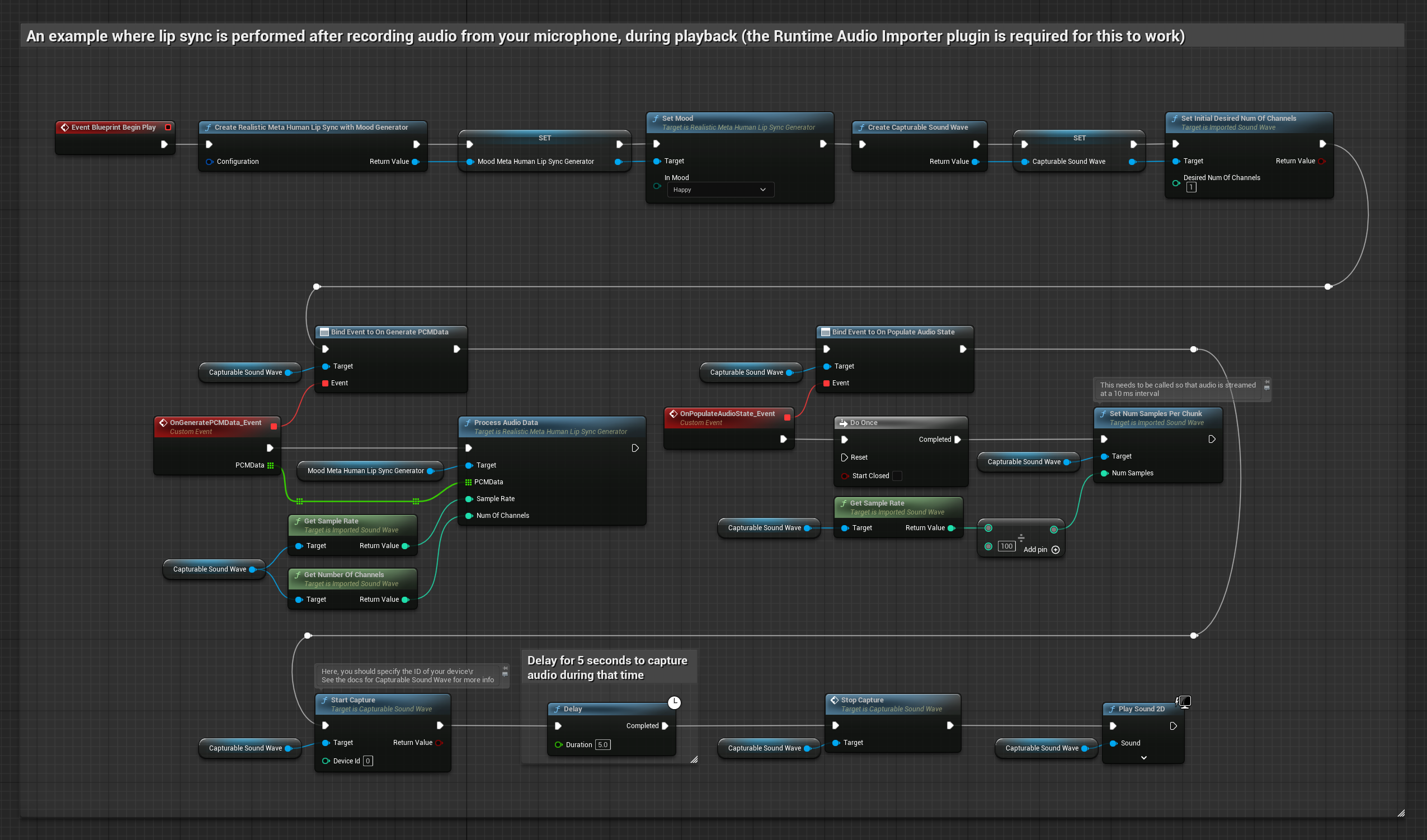
This approach captures audio from a microphone, then plays it back with lip sync:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Create a Capturable Sound Wave using Runtime Audio Importer
- For Linux with Pixel Streaming, use Pixel Streaming Capturable Sound Wave instead
- Start audio capture from the microphone
- Before playing back the capturable sound wave, bind to its
OnGeneratePCMDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
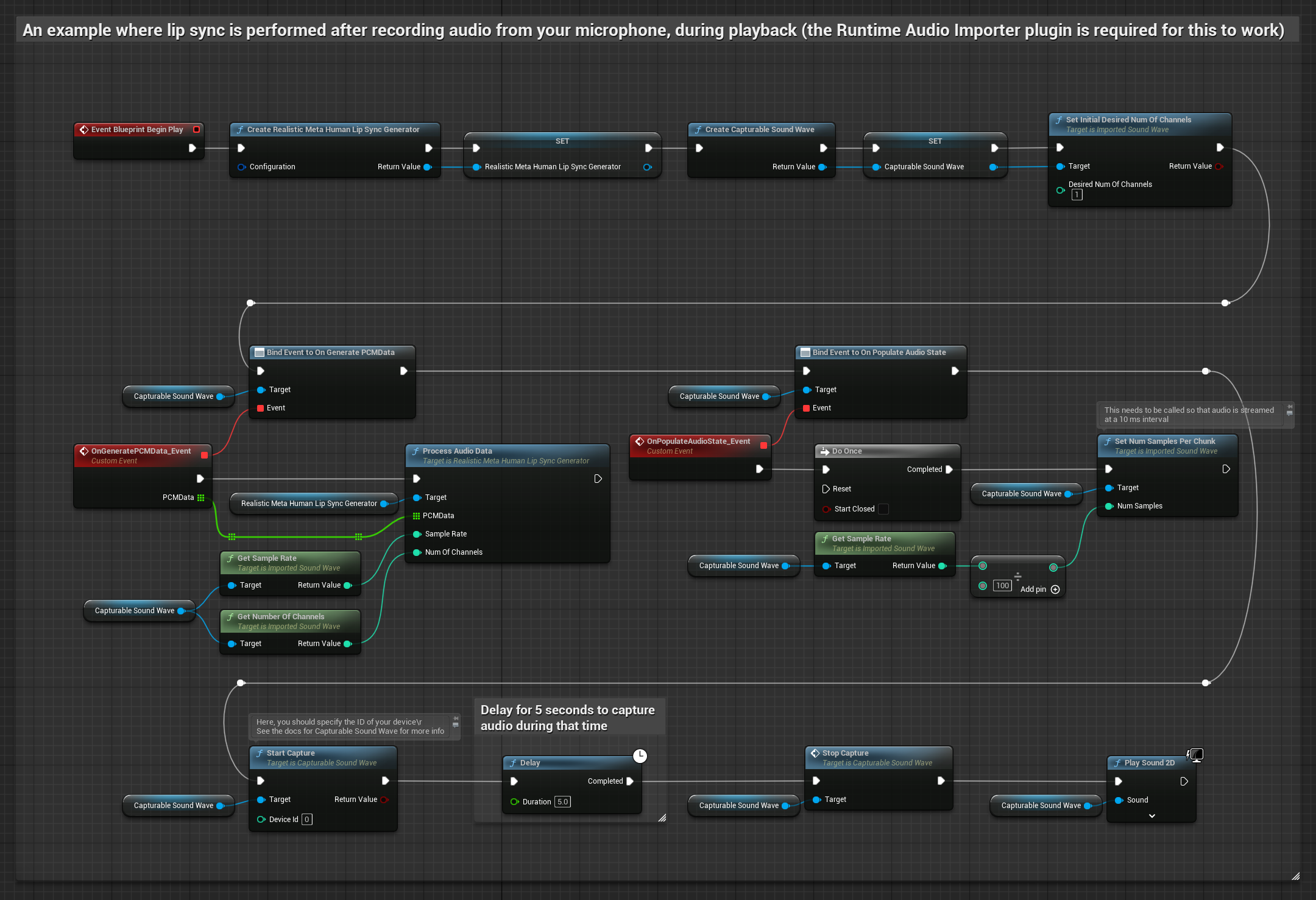
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
- Regular
- Streaming
This approach synthesizes speech from text using local TTS and performs lip sync:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Use Runtime Text To Speech to generate speech from text
- Use Runtime Audio Importer to import the synthesized audio
- Before playing back the imported sound wave, bind to its
OnGeneratePCMDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator
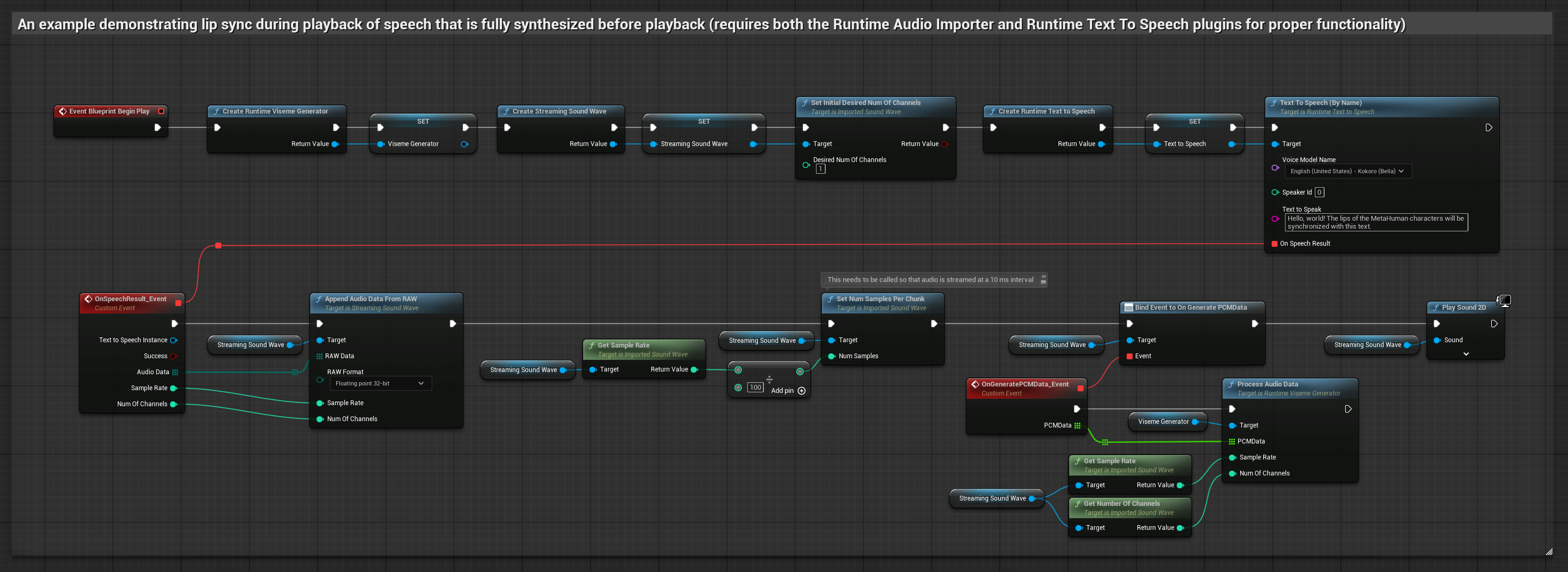
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
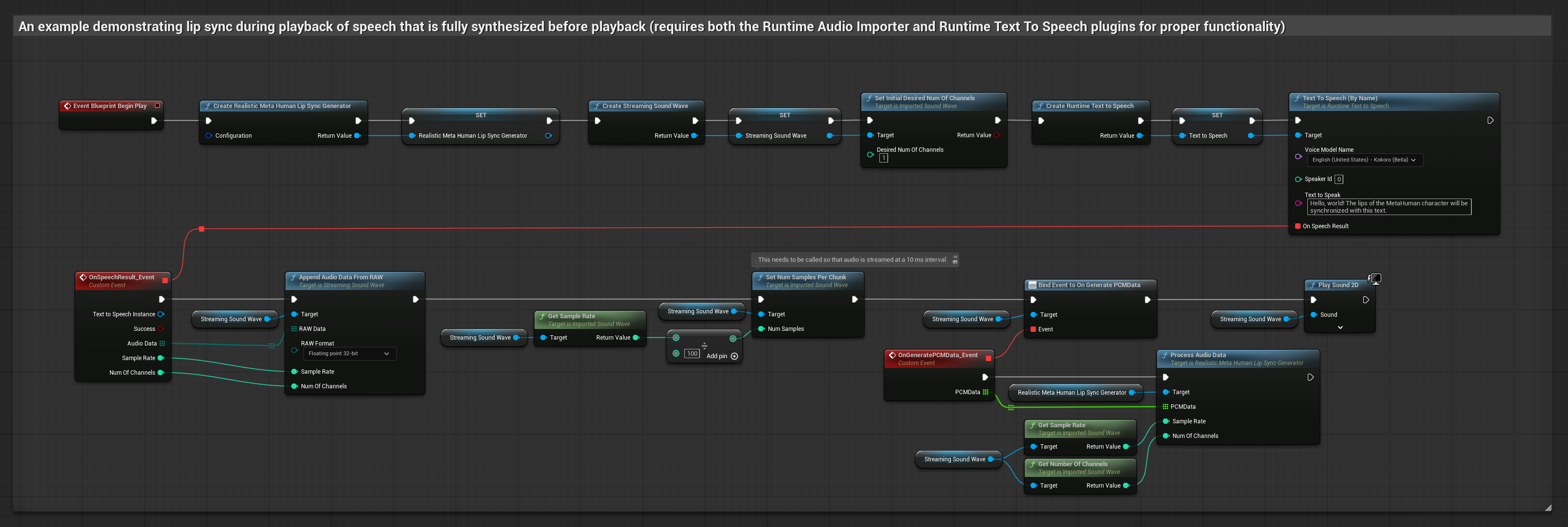
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
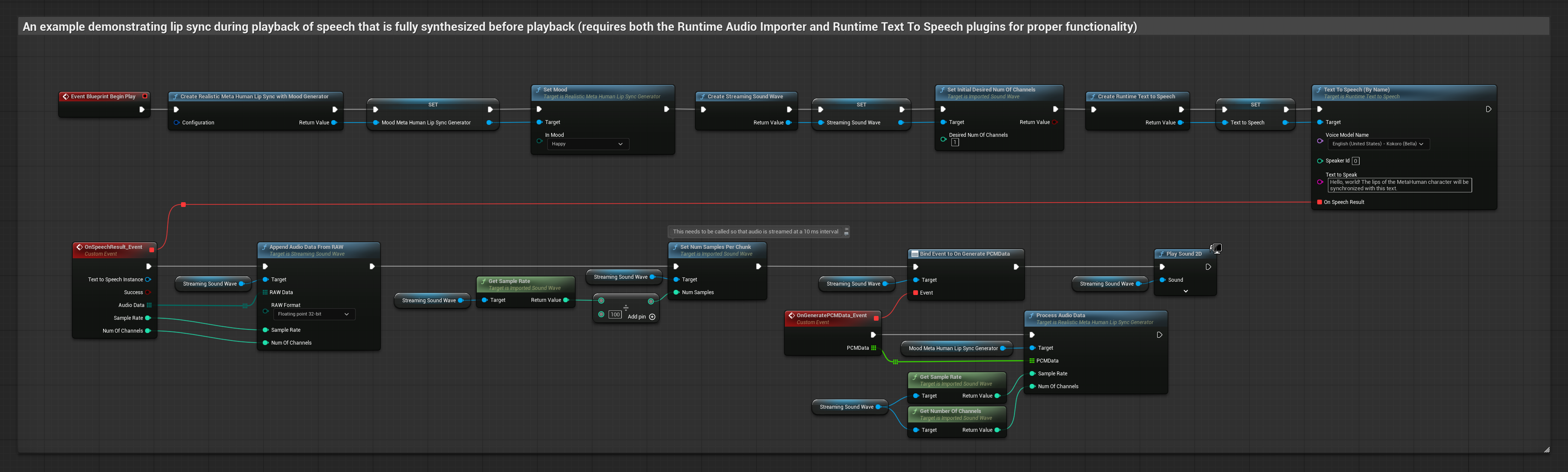
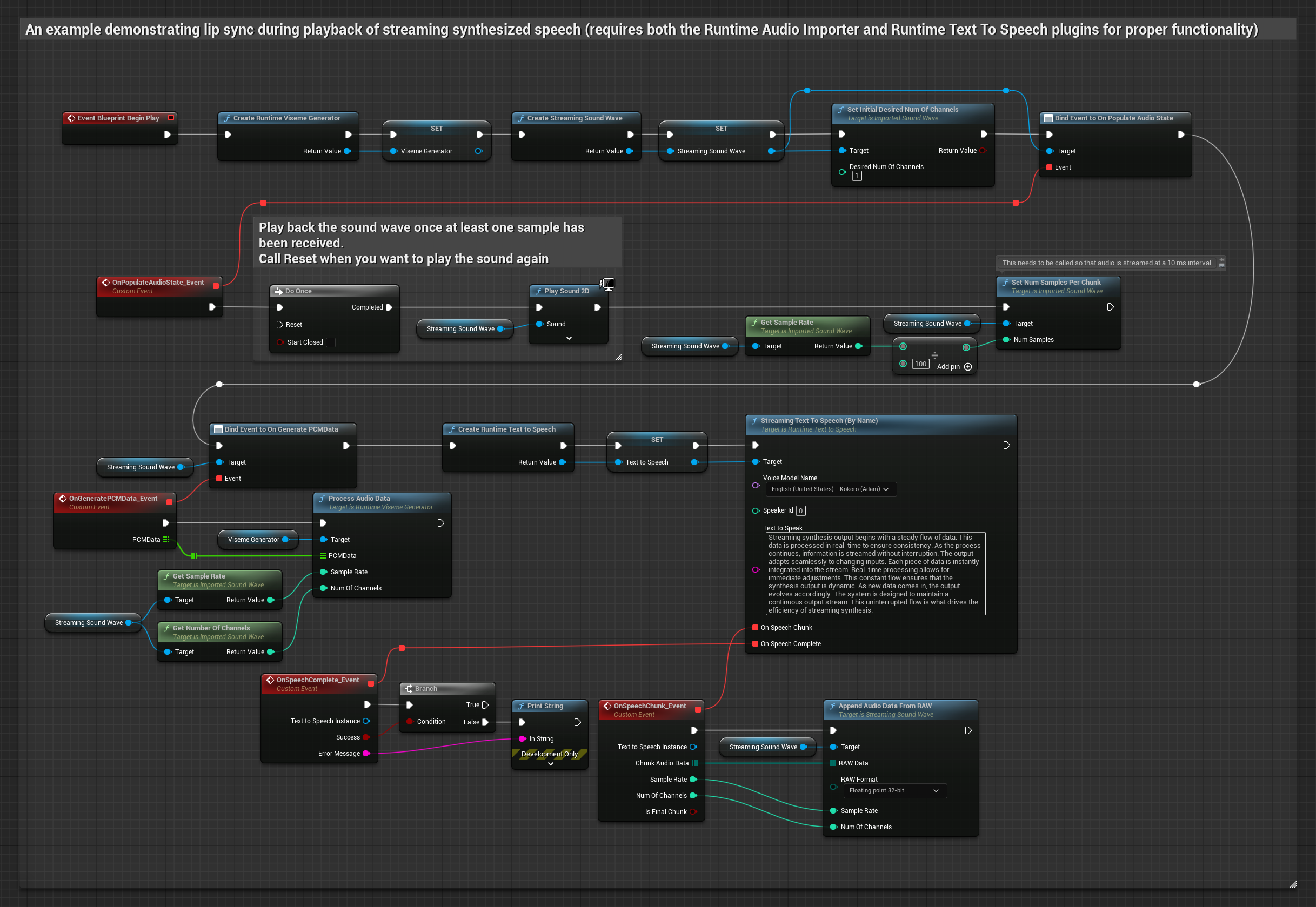
This approach uses streaming text-to-speech synthesis with real-time lip sync:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Use Runtime Text To Speech to generate streaming speech from text
- Use Runtime Audio Importer to import the synthesized audio
- Before playing back the streaming sound wave, bind to its
OnGeneratePCMDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator
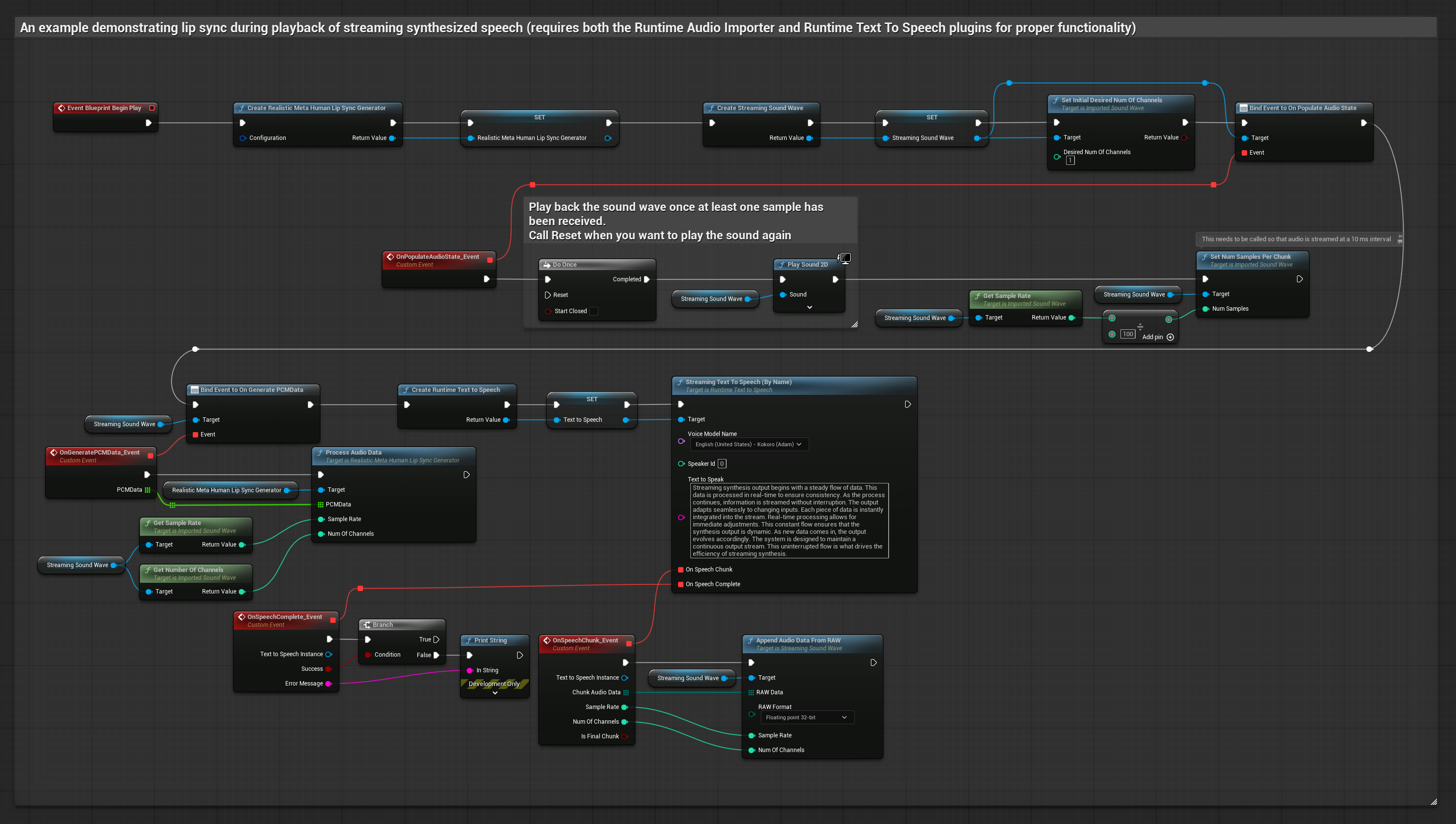
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
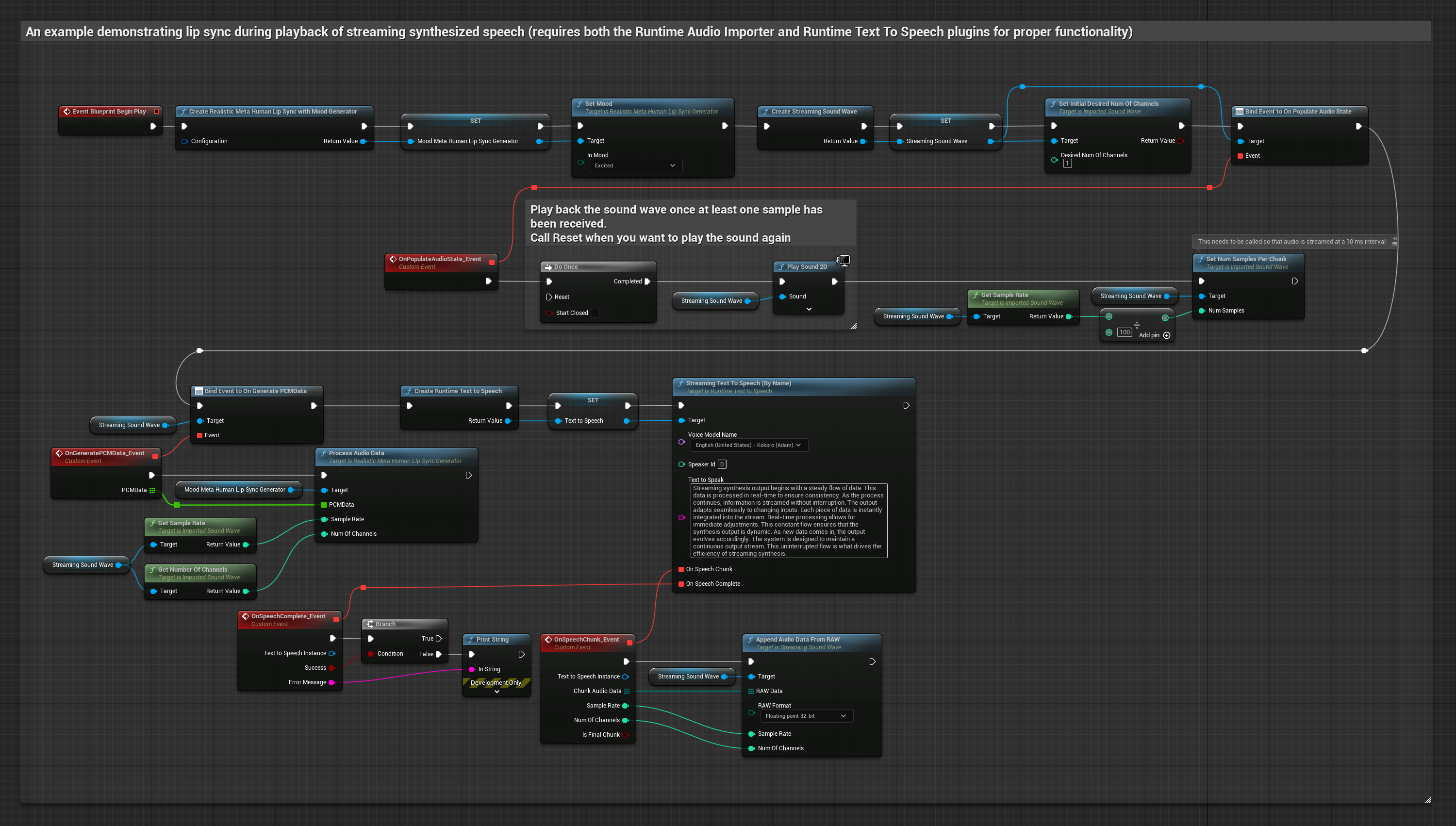
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
- Regular
- Streaming
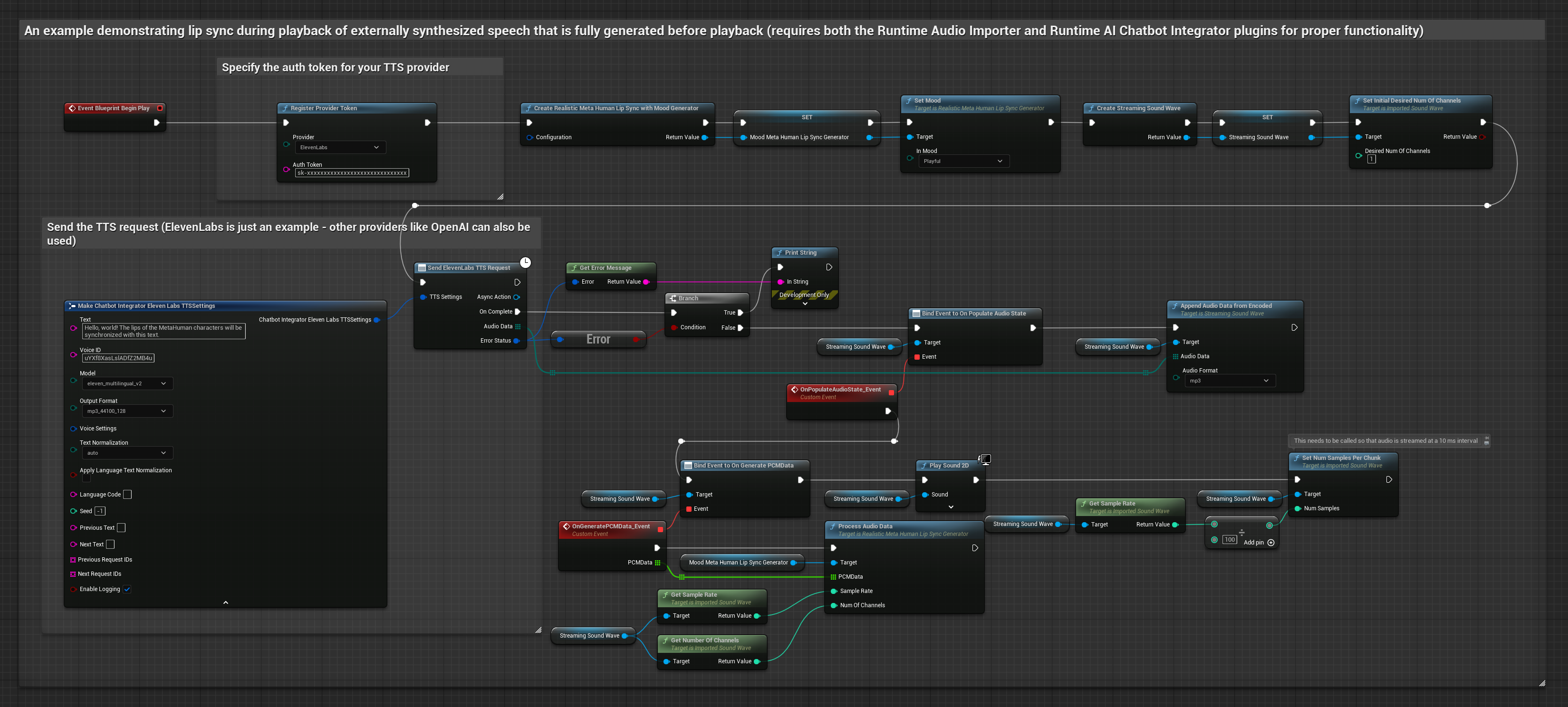
This approach uses the Runtime AI Chatbot Integrator plugin to generate synthesized speech from AI services (OpenAI or ElevenLabs) and perform lip sync:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Use Runtime AI Chatbot Integrator to generate speech from text using external APIs (OpenAI, ElevenLabs, etc.)
- Use Runtime Audio Importer to import the synthesized audio data
- Before playing back the imported sound wave, bind to its
OnGeneratePCMDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator
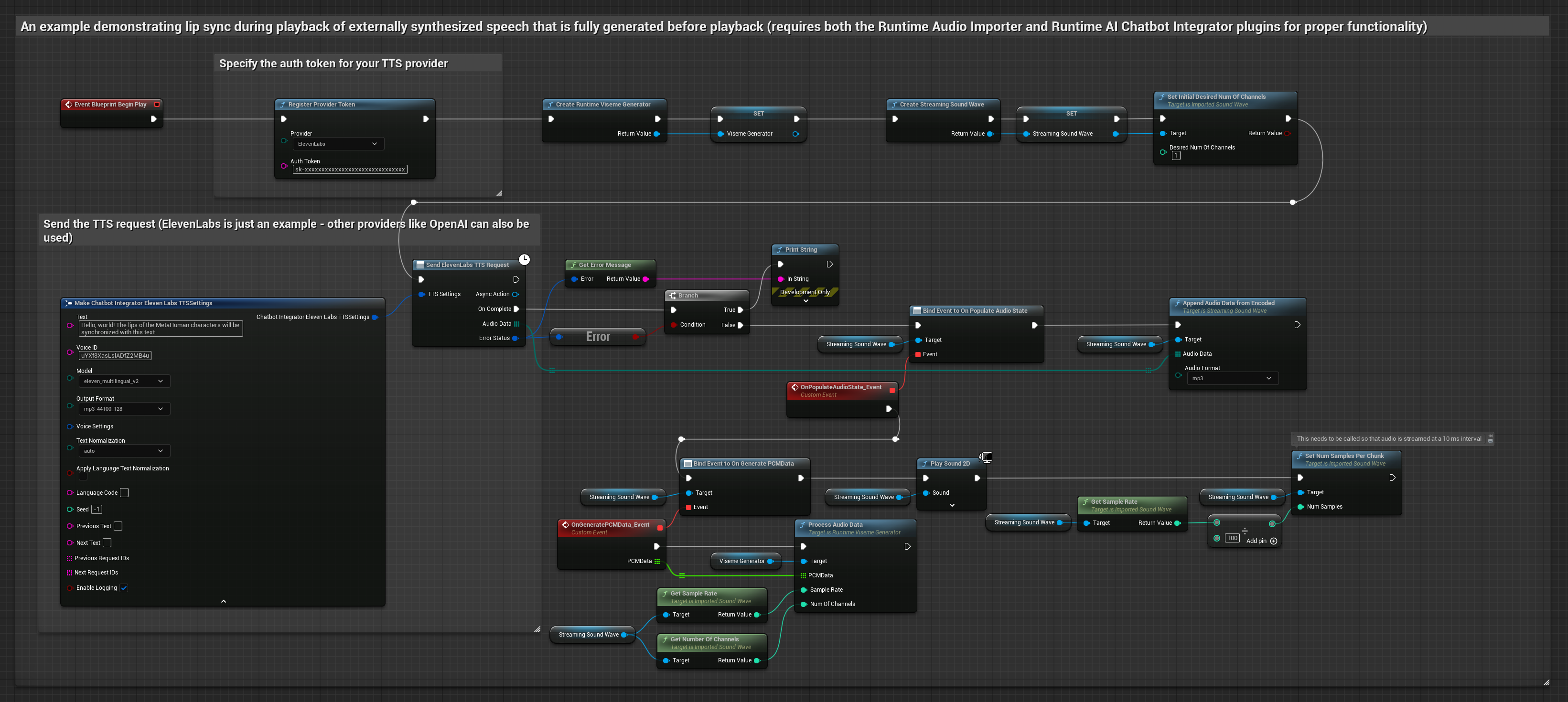
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
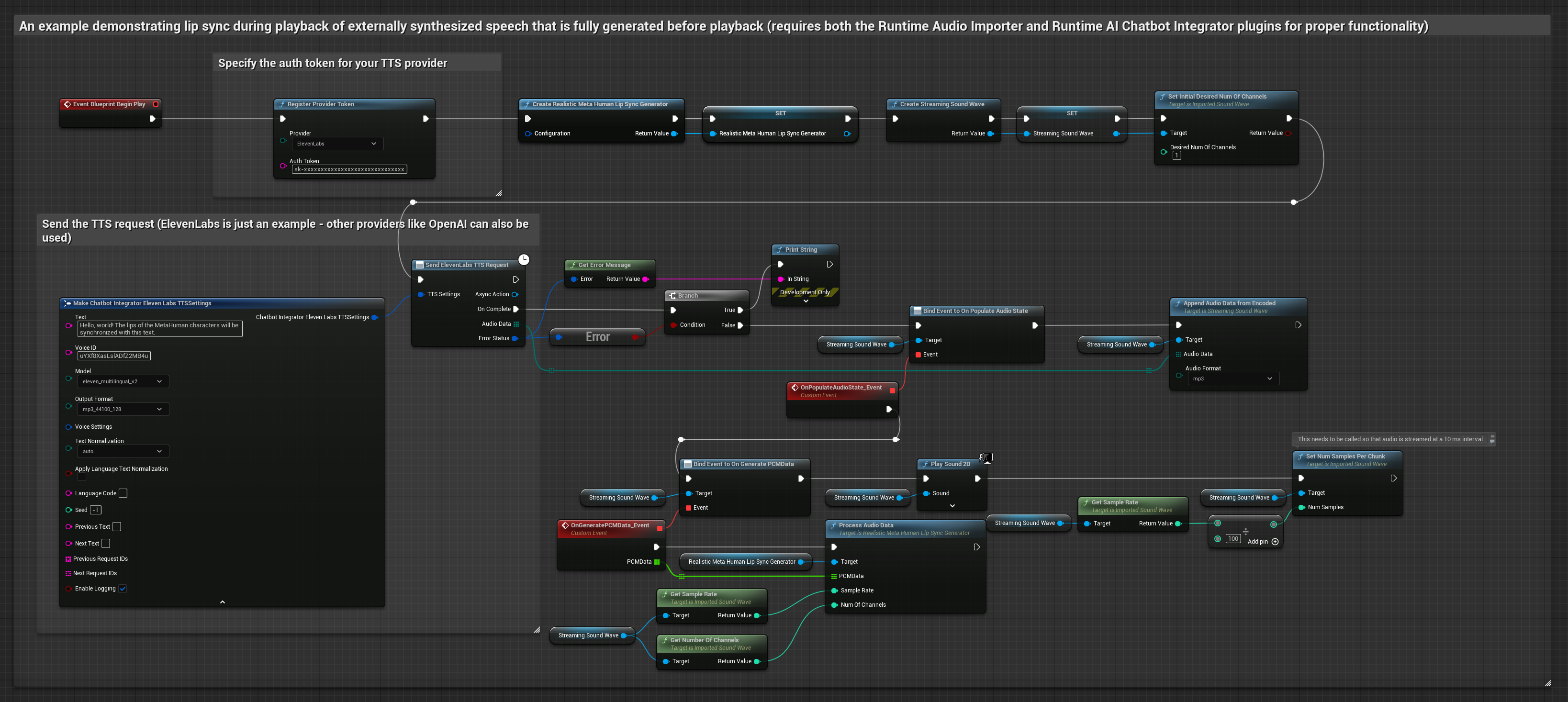
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
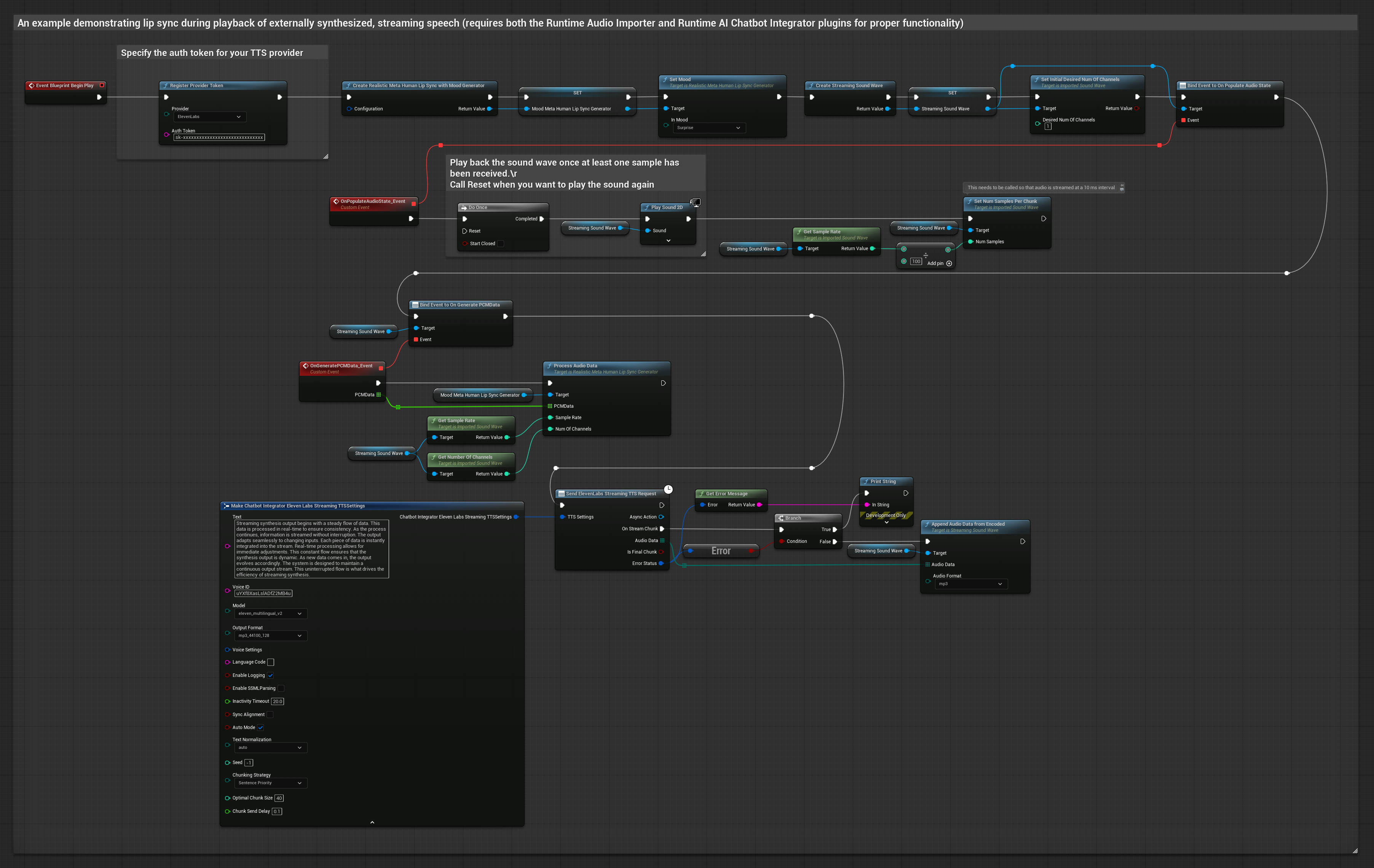
This approach uses the Runtime AI Chatbot Integrator plugin to generate synthesized streaming speech from AI services (OpenAI or ElevenLabs) and perform lip sync:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Use Runtime AI Chatbot Integrator to connect to streaming TTS APIs (like ElevenLabs Streaming API)
- Use Runtime Audio Importer to import the synthesized audio data
- Before playing back the streaming sound wave, bind to its
OnGeneratePCMDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator
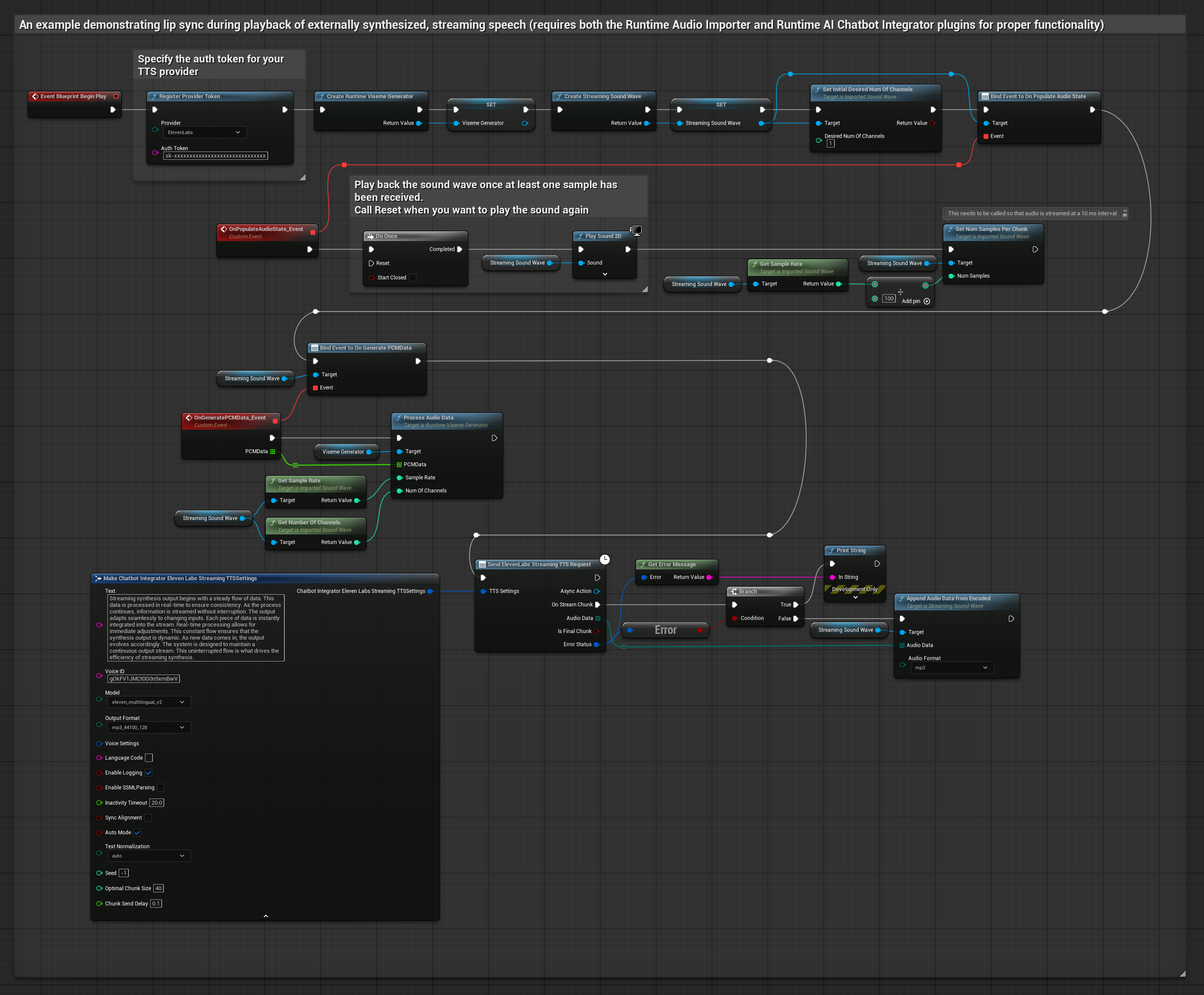
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
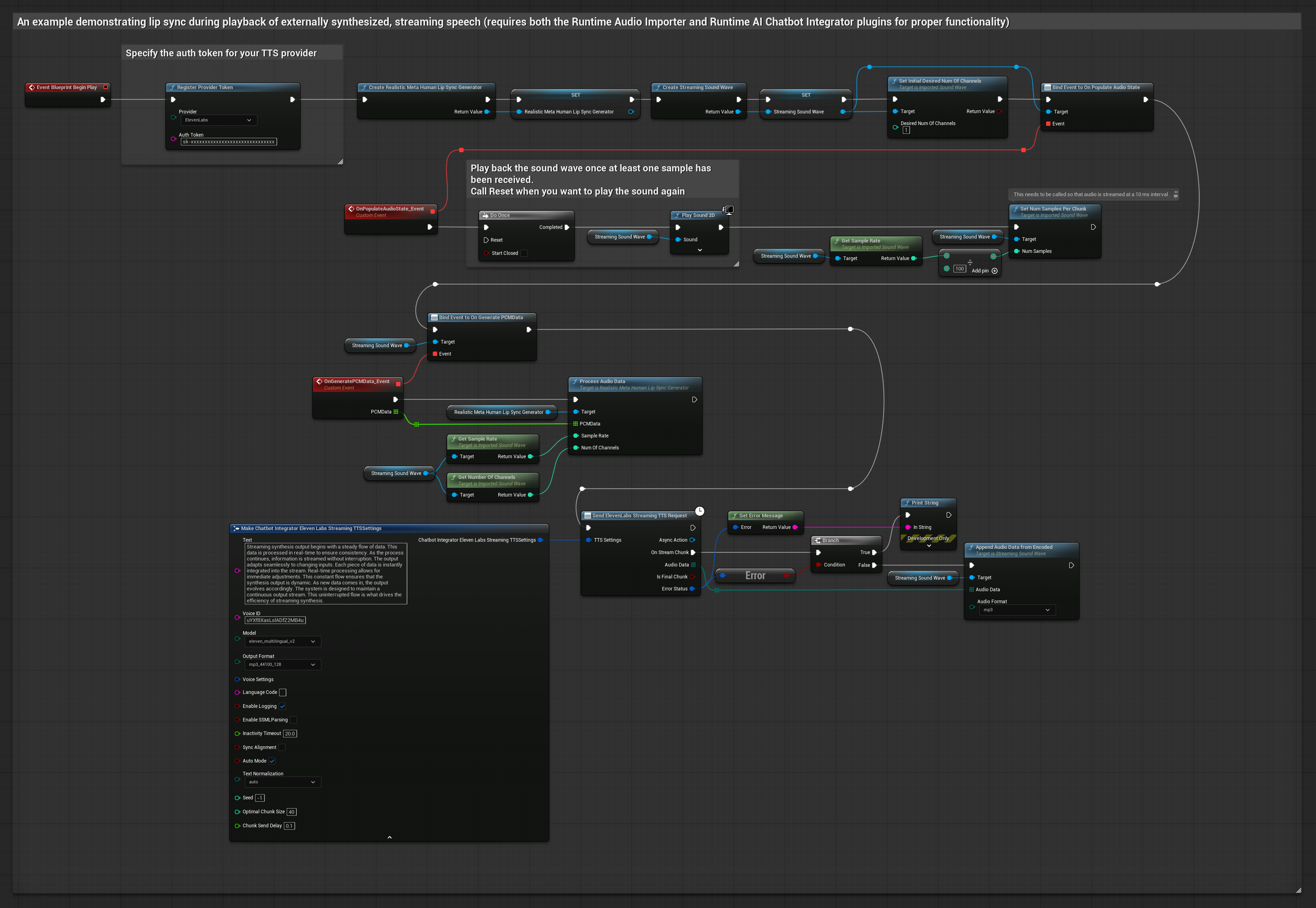
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
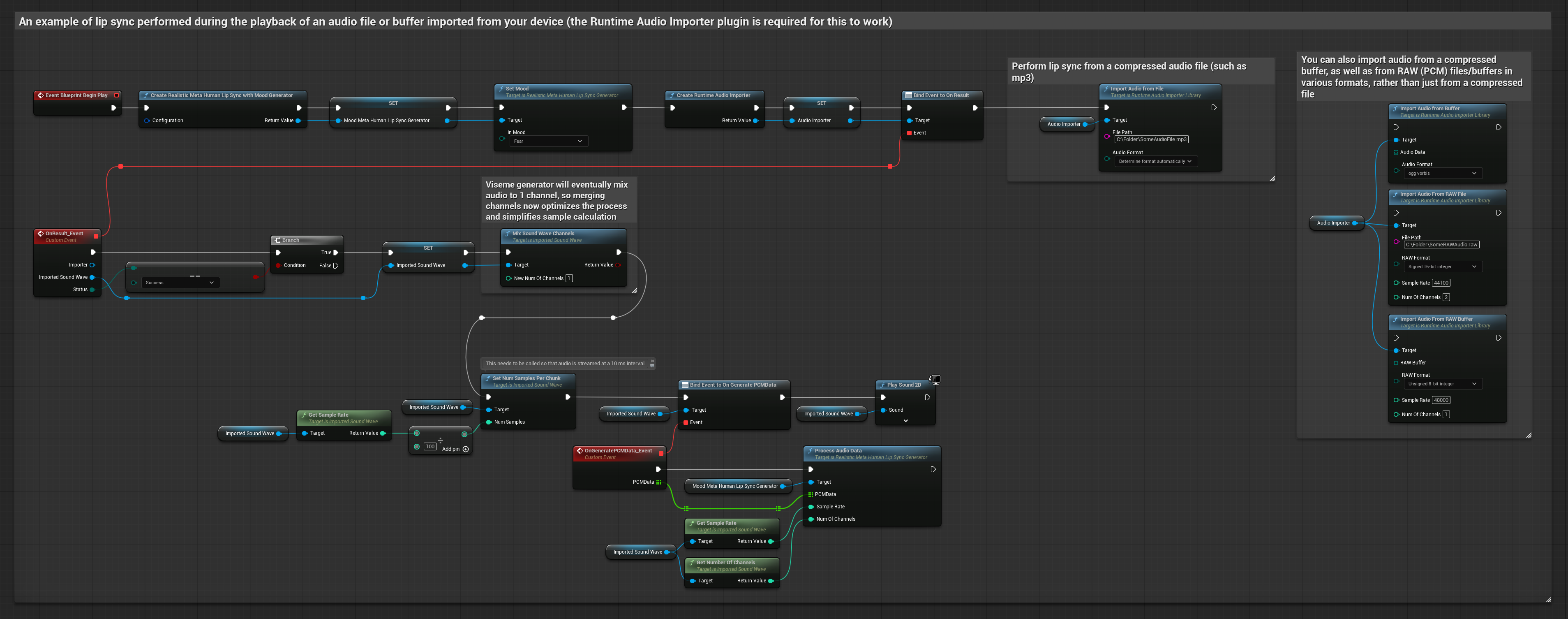
This approach uses pre-recorded audio files or audio buffers for lip sync:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Use Runtime Audio Importer to import an audio file from disk or memory
- Before playing back the imported sound wave, bind to its
OnGeneratePCMDatadelegate - In the bound function, call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator - Play the imported sound wave and observe the lip sync animation
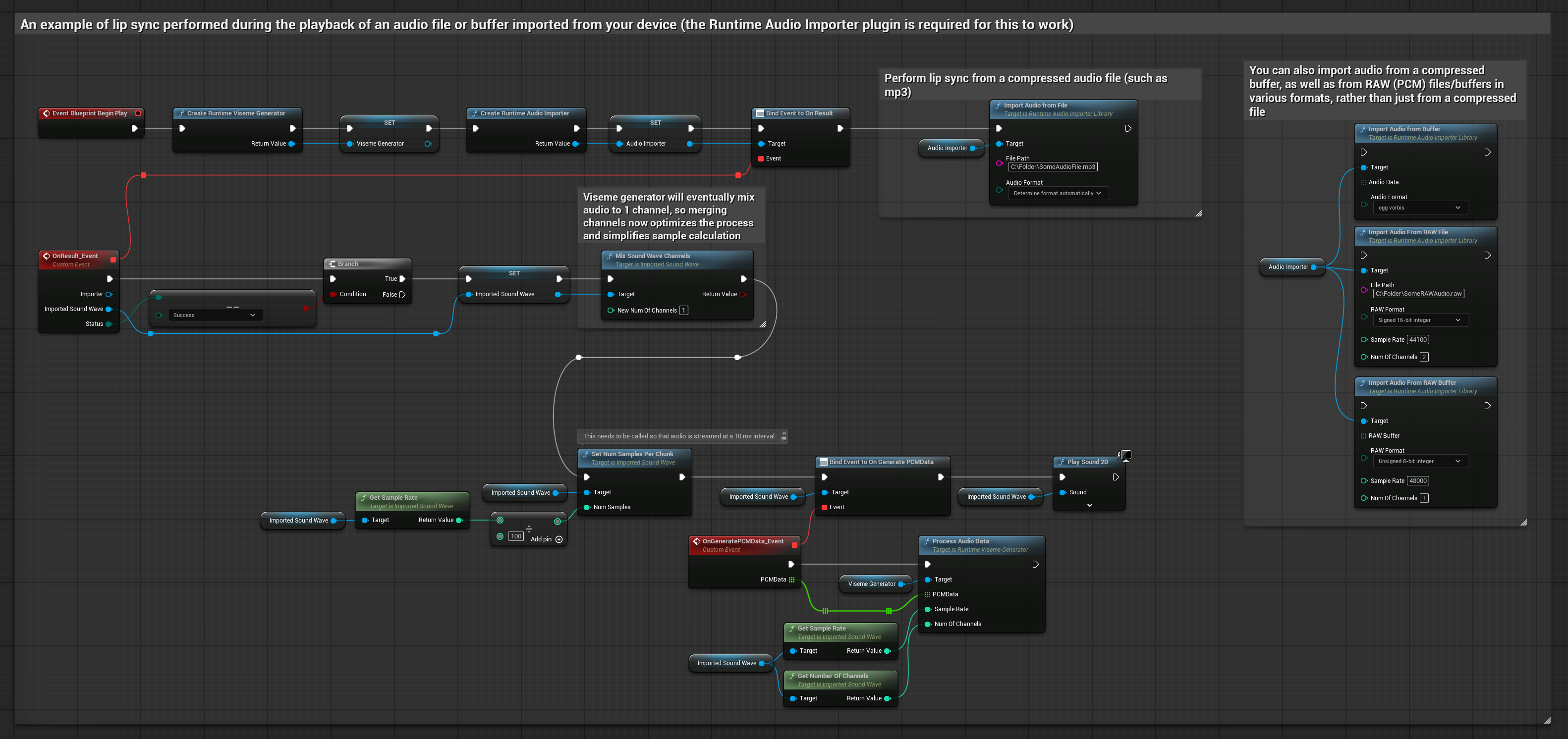
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
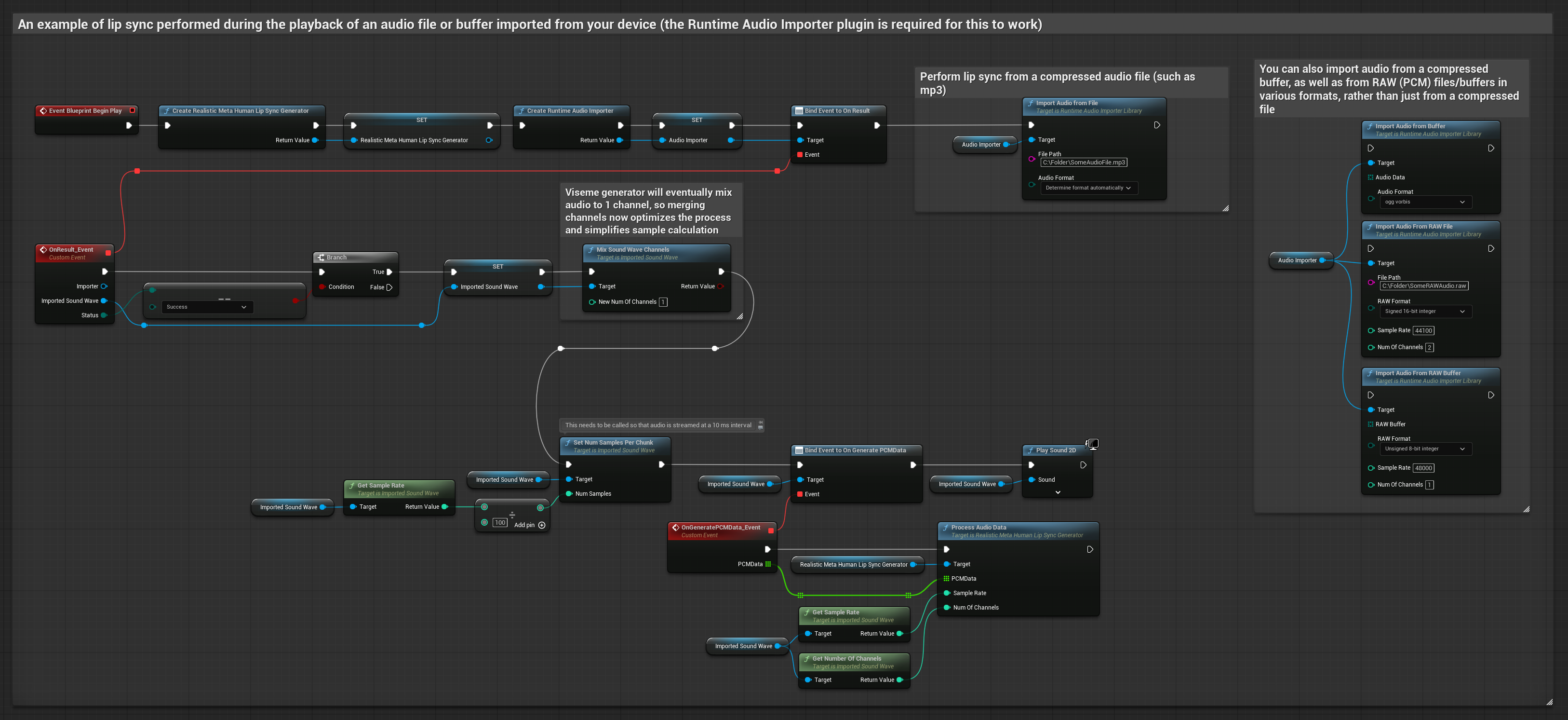
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
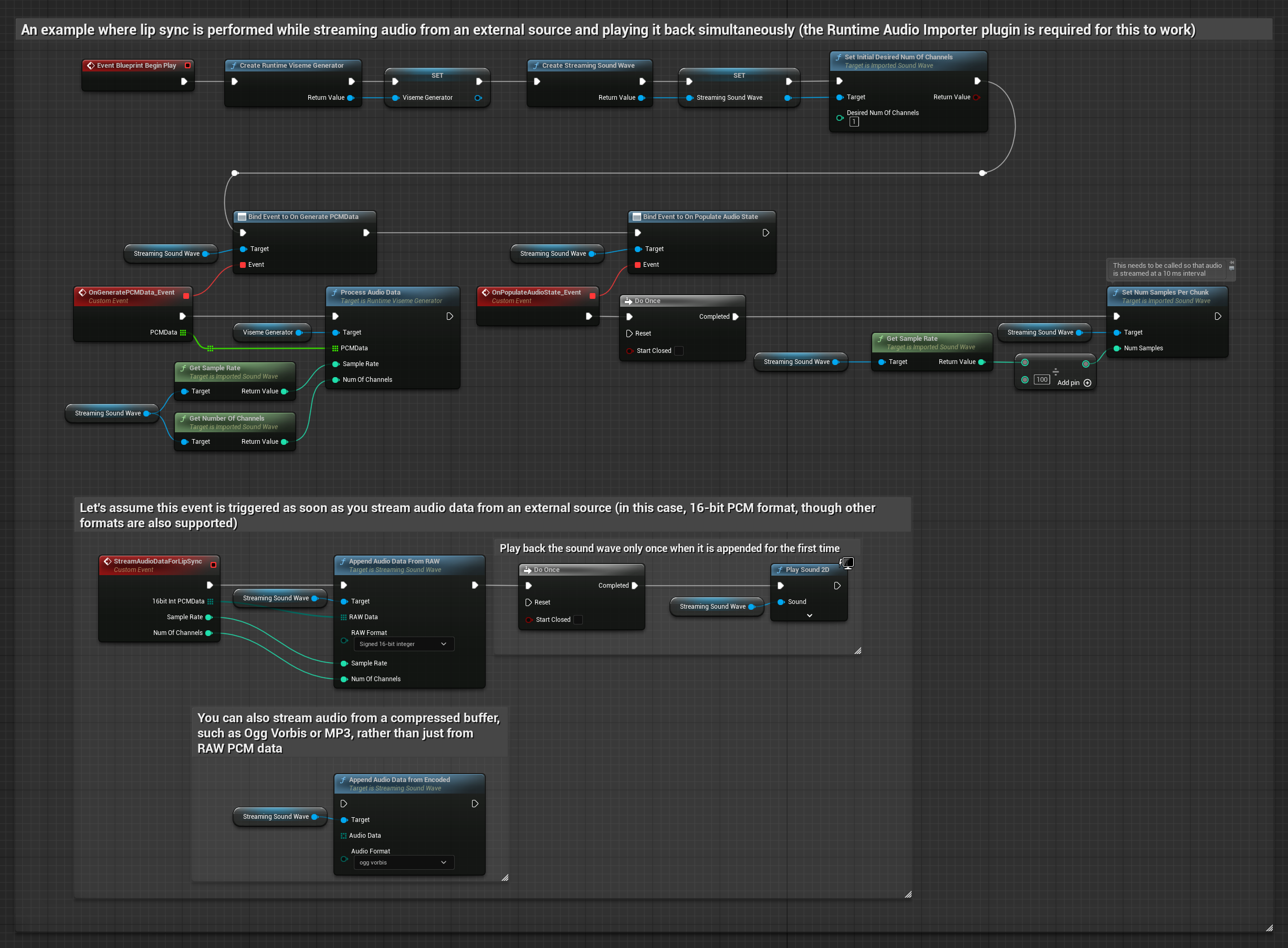
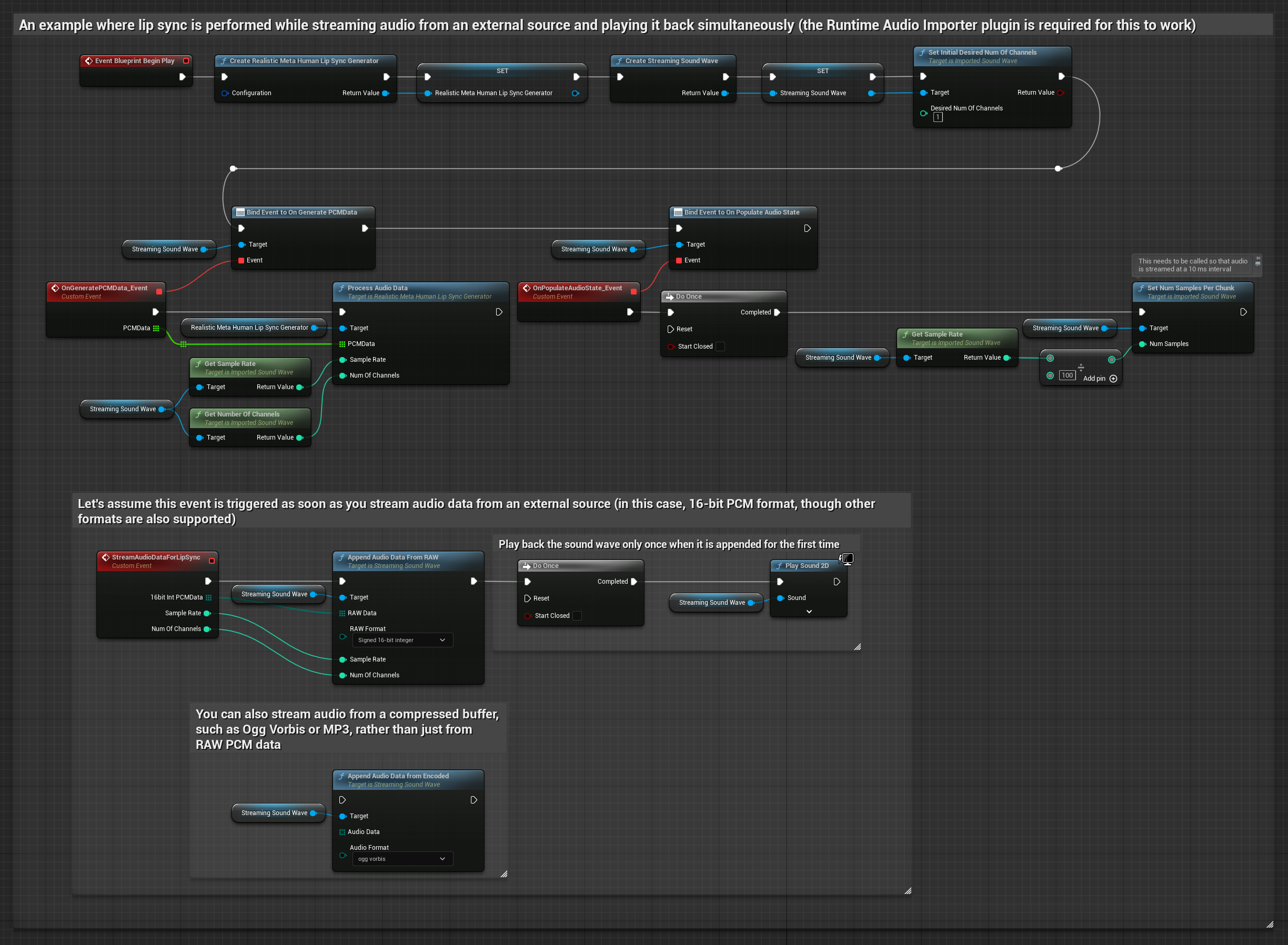
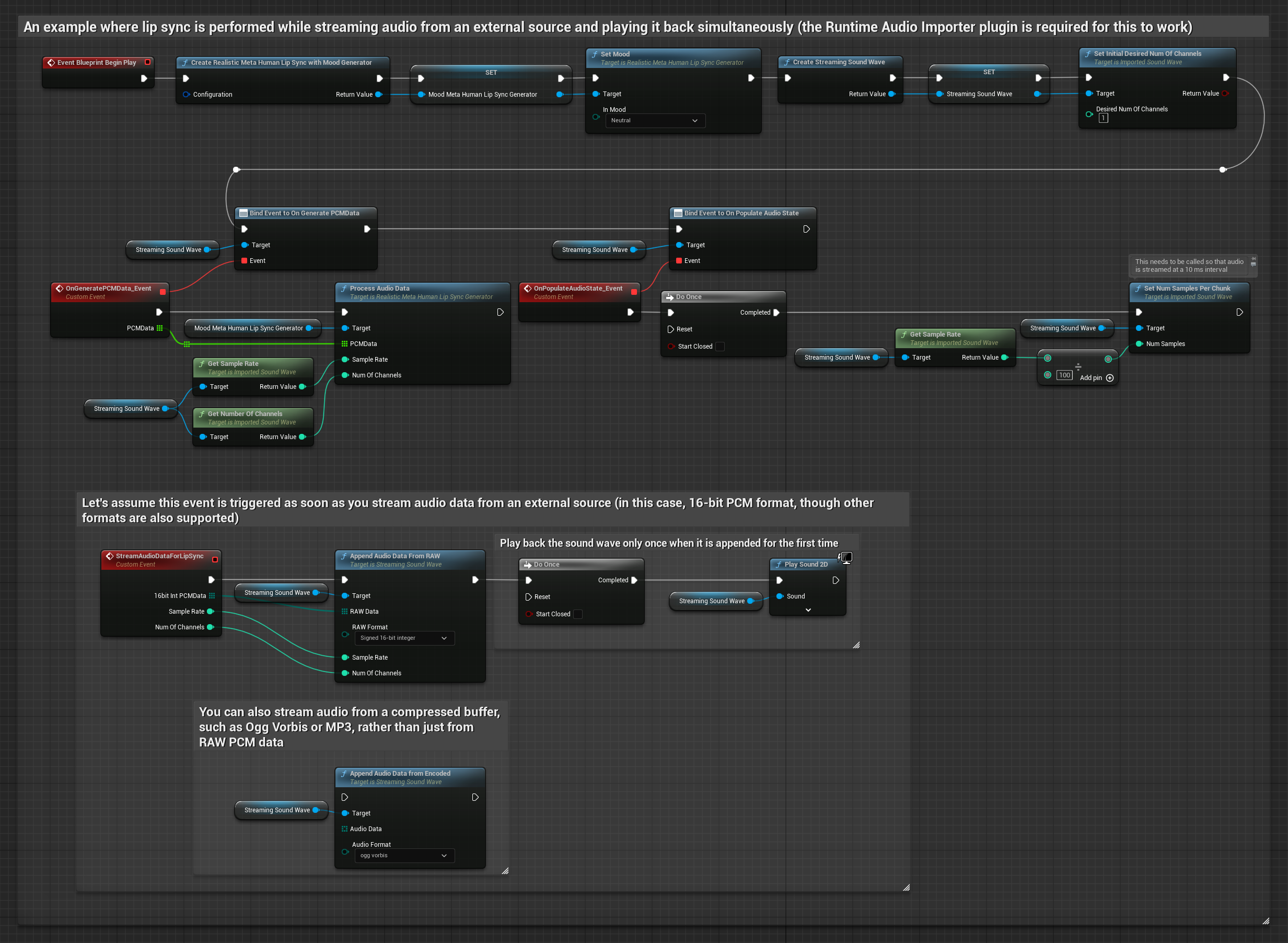
For streaming audio data from a buffer, you need:
- Standard Model
- Realistic Model
- Mood-Enabled Realistic Model
- Audio data in float PCM format (an array of floating-point samples) available from your streaming source (or use Runtime Audio Importer to support more formats)
- The sample rate and number of channels
- Call
ProcessAudioDatafrom your Runtime Viseme Generator with these parameters as audio chunks become available
The Realistic Model uses the same audio processing workflow as the Standard Model, but with the RealisticLipSyncGenerator variable instead of VisemeGenerator.
The Mood-Enabled Model uses the same audio processing workflow, but with the MoodMetaHumanLipSyncGenerator variable and additional mood configuration capabilities.
Note: When using streaming audio sources, make sure to manage audio playback timing appropriately to avoid distorted playback. See the Streaming Sound Wave documentation for more information.
Processing Performance Tips
-
Chunk Size: If you want to process audio data in smaller chunks for more responsive lip sync, adjust the calculation in the
SetNumSamplesPerChunkfunction. For example, dividing the sample rate by 150 (streaming every ~6.67 ms) instead of 100 (streaming every 10 ms) will provide more frequent lip sync updates. -
Buffer Management: The mood-enabled model processes audio in 320-sample frames (20ms at 16kHz). Ensure your audio input timing aligns with this for optimal performance.
-
Generator Recreation: For reliable operation with Realistic models, recreate the generator each time you want to feed new audio data after a period of inactivity.
Next Steps
Once you have audio processing set up, you may want to:
- Learn about Configuration options to fine-tune your lip sync behavior
- Add laughter animation for enhanced expressiveness
- Combine lip sync with existing facial animations using the layering techniques described in the Configuration guide