Import Audio
Overview
The process of importing audio at runtime can be broken down into several steps:
- Create a Runtime Audio Importer
- Bind to the needed delegates (OnProgress and OnResult)
- Import audio from a file or buffer
- Play the imported sound wave obtained from the OnResult delegate (more info is here)
Ensure that both Runtime Audio Importer and Sound Wave instances are not prematurely garbage collected by maintaining a hard reference to them, which can be done by assigning them to separate variables using UPROPERTY(), TStrongObjectPtr, or any other method that prevents the object from being destroyed.
Supported Audio Formats
Runtime Audio Importer supports importing the following audio formats:
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| MP3 | MPEG-1/2/2.5 Audio Layer I/II/III |
| WAV | Waveform Audio File Format |
| FLAC | Free Lossless Audio Codec |
| OGG VORBIS | Ogg container with Vorbis audio |
| OGG OPUS | Ogg container with Opus audio |
| BINK | Bink Audio |
| RAW (PCM) | Uncompressed Pulse-Code Modulation audio data (Int8, UInt8, Int16, UInt16, Int32, UInt32, Float32) |
When importing audio, you can either specify the format explicitly or use automatic format detection based on file extension or content.
Streaming Audio Imports
For streaming scenarios where audio data is received incrementally (e.g., from a server, real-time capture, or network streams), consider using Streaming Sound Waves.
This method provides a continuous way to append audio data to the same sound wave's buffer, making it suitable for live streams or large files processed in chunks. See the Streaming Sound Wave documentation for more details.
Basic Implementation Steps
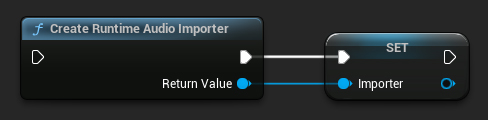
1. Create Runtime Audio Importer
First, you need to create a Runtime Audio Importer object. You should ensure it is treated as a strong reference by the garbage collector.
- Blueprint
- C++
// UPROPERTY() is used here to prevent the object from being prematurely garbage collected
UPROPERTY()
class URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* Importer;
Importer = URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary::CreateRuntimeAudioImporter();
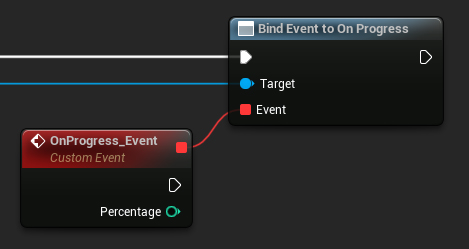
2. Bind to OnProgress Delegate
To track the progress of importing audio data, you can bind to the OnProgress (Blueprints) / OnProgressNative (C++) delegate.
- Blueprint
- C++
// Assuming Importer is a UE reference to a URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary object
// AddWeakLambda is used just as an example. You can use any other method to bind the delegate, such as AddUObject, AddUFunction, etc.
Importer->OnProgressNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [](int32 Percentage)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Import progress: %d"), Percentage);
});
This will allow you to monitor the progress and, for example, implement a loading screen.
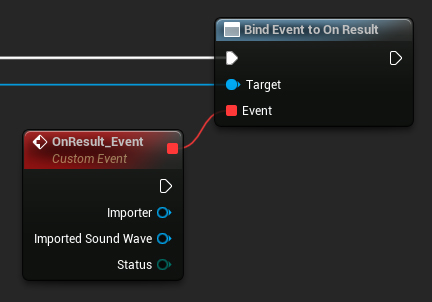
3. Bind to OnResult Delegate
To be notified when the audio data import process is complete and to access the reference of the resulting sound wave, you must bind to the OnResult (Blueprints) / OnResultNative (C++) delegate.
- Blueprint
- C++
// Assuming Importer is a UE reference to a URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary object
// AddWeakLambda is used just as an example. You can use any other method to bind the delegate, such as AddUObject, AddUFunction, etc.
Importer->OnResultNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [](URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* Importer, UImportedSoundWave* ImportedSoundWave, ERuntimeImportStatus Status)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Import result: %s"), *UEnum::GetValueAsString(Status));
});
Make sure the imported sound wave is treated as a strong reference by the garbage collector to prevent unwanted premature garbage collection. This can be done by placing it as a separate variable in Blueprints.
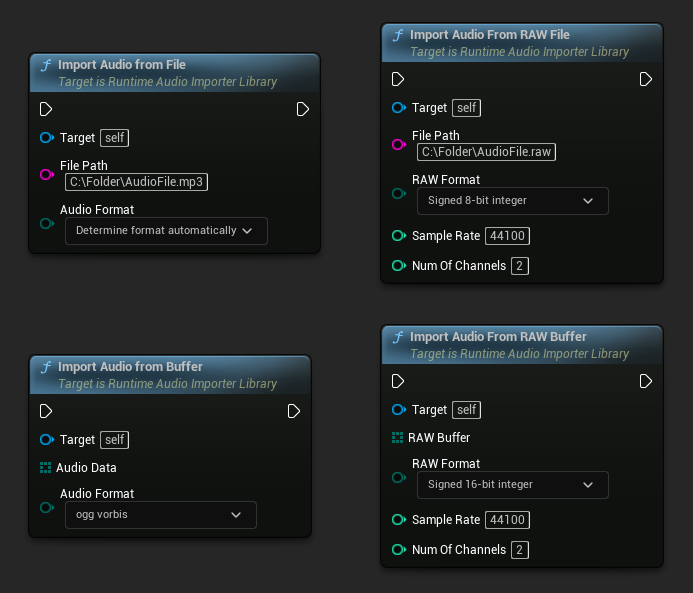
4. Start Audio Import
Begin the audio import process by calling the relevant function, which can handle both compressed and uncompressed audio data formats.
- Blueprint
- C++
// Assuming Importer is a UE reference to a URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary object
// Import audio from a file
Importer->ImportAudioFromFile(TEXT("C:/Folder/AudioFile.mp3"), ERuntimeAudioFormat::Auto);
// Import audio from a buffer
TArray<uint8> AudioData = ...; // Fill the array with your audio data
Importer->ImportAudioFromBuffer(MoveTemp(AudioData), ERuntimeAudioFormat::OggVorbis);
// Import audio from a RAW file
Importer->ImportAudioFromRAWFile(TEXT("C:/Folder/AudioFile.raw"), ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Int8, 44100, 2);
// Import audio from a RAW buffer
TArray<uint8> RAWBuffer = ...; // Fill the array with your PCM int 16-bit audio data
Importer->ImportAudioFromRAWBuffer(MoveTemp(RAWBuffer), ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Int16, 44100, 2);
Utility Functions
Finding Audio Files
You can scan a directory for supported audio files:
- Blueprint
- C++
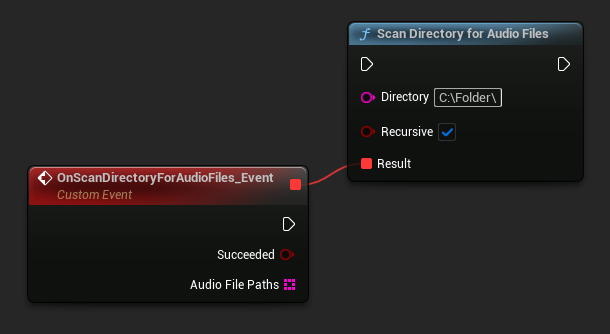
URuntimeAudioUtilities::ScanDirectoryForAudioFiles(TEXT("C:/Folder/"), true,
FOnScanDirectoryForAudioFilesResultNative::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](bool bSucceeded, const TArray<FString>& AudioFilePaths)
{
// Handle the result
}));
Complete Example
Here's a full implementation example for importing audio:
- Blueprint
- C++
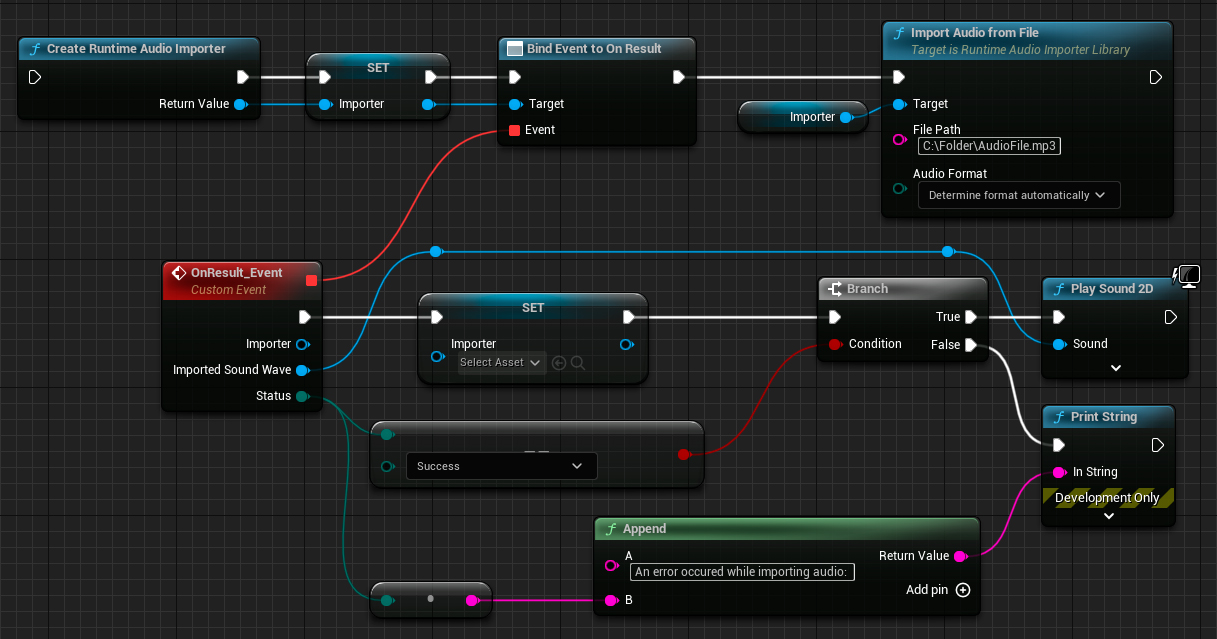
This is a basic code example for importing audio from a file.
The example uses the ImportAudioExample function located in the UImportAudioClassExample class within the EXAMPLEMODULE module.
To successfully run the example, make sure to add the RuntimeAudioImporter module to either PublicDependencyModuleNames or PrivateDependencyModuleNames in the .Build.cs file, as well as to your project's .uproject file.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "UObject/Object.h"
#include "ImportAudioClassExample.generated.h"
UCLASS(BlueprintType)
class EXAMPLEMODULE_API UImportAudioClassExample : public UObject
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
void ImportAudioExample();
private:
// Please pay attention to making the RuntimeAudioImporter a hard reference, such as using UPROPERTY(), to prevent it from being prematurely garbage collected
UPROPERTY()
class URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* RuntimeAudioImporter;
};
#include "ImportAudioClassExample.h"
#include "RuntimeAudioImporterLibrary.h"
void UImportAudioClassExample::ImportAudioExample()
{
RuntimeAudioImporter = URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary::CreateRuntimeAudioImporter();
if (!IsValid(RuntimeAudioImporter))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to create audio importer"));
return;
}
RuntimeAudioImporter->OnProgressNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [](int32 Percentage)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Audio importing percentage: %d"), Percentage);
});
RuntimeAudioImporter->OnResultNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* Importer, UImportedSoundWave* ImportedSoundWave, ERuntimeImportStatus Status)
{
if (Status == ERuntimeImportStatus::SuccessfulImport)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Warning, TEXT("Successfully imported audio with sound wave %s"), *ImportedSoundWave->GetName());
// Here you can handle ImportedSoundWave playback, like "UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), ImportedSoundWave);"
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to import audio"));
}
RuntimeAudioImporter = nullptr;
});
RuntimeAudioImporter->ImportAudioFromFile(TEXT("C:/Folder/Example.mp3"), ERuntimeAudioFormat::Auto);
}