كيفية استخدام الإضافة
تقوم إضافة Runtime Text To Speech بتحويل النص إلى كلام باستخدام نماذج صوتية قابلة للتحميل. تتم إدارة هذه النماذج في إعدادات الإضافة داخل المحرر، ويتم تنزيلها وتعبئتها للاستخدام أثناء التشغيل. اتبع الخطوات أدناه للبدء.
جانب المحرر
قم بتنزيل نماذج الصوت المناسبة لمشروعك كما هو موضح هنا. يمكنك تنزيل عدة نماذج صوتية في نفس الوقت.
جانب التشغيل
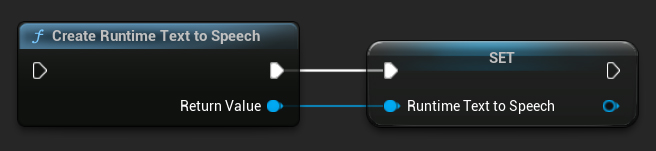
قم بإنشاء المُركِّب باستخدام الدالة CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech. تأكد من الحفاظ على مرجع له (مثل متغير منفصل في Blueprints أو UPROPERTY في ++C) لمنعه من جمع القمامة.
- Blueprint
- C++
// Create the Runtime Text To Speech synthesizer in C++
URuntimeTextToSpeech* Synthesizer = URuntimeTextToSpeech::CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech();
// Ensure the synthesizer is referenced correctly to prevent garbage collection (e.g. as a UPROPERTY)
توليد الكلام
يقدم البرنامج المساعد وضعين لتوليد الكلام من النص:
- تحويل النص إلى كلام العادي: يقوم بتوليد النص بالكامل وإرجاع الصوت المكتمل عند الانتهاء
- تحويل النص إلى كلام المتدفق: يوفر مقاطع الصوت فور إنشائها، مما يسمح بالمعالجة في الوقت الفعلي
يدعم كل وضع طريقتين لاختيار نماذج الصوت:
- بالاسم: اختر نموذج صوت باسمه (موصى به لـ UE 5.4+)
- بالكائن: اختر نموذج صوت بالإشارة المباشرة (موصى به لـ UE 5.3 والإصدارات الأقدم)
تحويل النص إلى كلام العادي
بالاسم
- Blueprint
- C++
تكون وظيفة Text To Speech (By Name) أكثر ملاءمة في Blueprints بدءًا من UE 5.4. تتيح لك اختيار نماذج الصوت من قائمة منسدلة للنماذج التي تم تنزيلها. في إصدارات UE الأقدم من 5.3، لا تظهر هذه القائمة المنسدلة، لذا إذا كنت تستخدم إصدارًا أقدم، فستحتاج إلى التكرار يدويًا عبر مصفوفة نماذج الصوت التي تم إرجاعها بواسطة GetDownloadedVoiceModels لاختيار النموذج الذي تحتاجه.
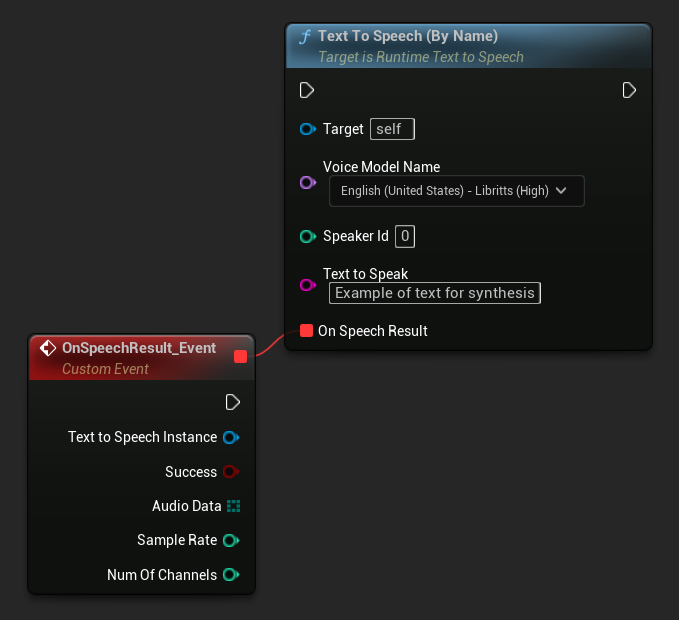
في C++، يمكن أن يكون اختيار نماذج الصوت أكثر تعقيدًا قليلاً بسبب عدم وجود قائمة منسدلة. يمكنك استخدام وظيفة GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames لاسترداد أسماء نماذج الصوت التي تم تنزيلها واختيار النموذج الذي تحتاجه. بعد ذلك، يمكنك استدعاء وظيفة TextToSpeechByName لتوليد النص باستخدام اسم نموذج الصوت المحدد.
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, just as an example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumChannels)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("TextToSpeech result: %s, AudioData size: %d, SampleRate: %d, NumChannels: %d"), bSuccess ? TEXT("Success") : TEXT("Failed"), AudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumChannels);
}));
return;
}
حسب الكائن
- Blueprint
- C++
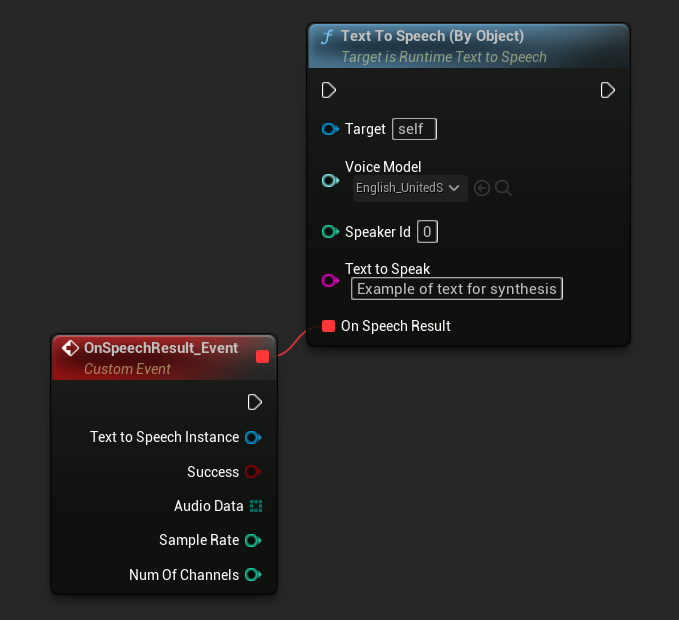
تعمل وظيفة Text To Speech (By Object) عبر جميع إصدارات Unreal Engine ولكنها تعرض نماذج الصوت كقائمة منسدلة من مراجع الأصول، وهو أقل بديهية. هذه الطريقة مناسبة لـ UE 5.3 والإصدارات السابقة، أو إذا كان مشروعك يتطلب مرجعًا مباشرًا إلى أصل نموذج صوتي لأي سبب.
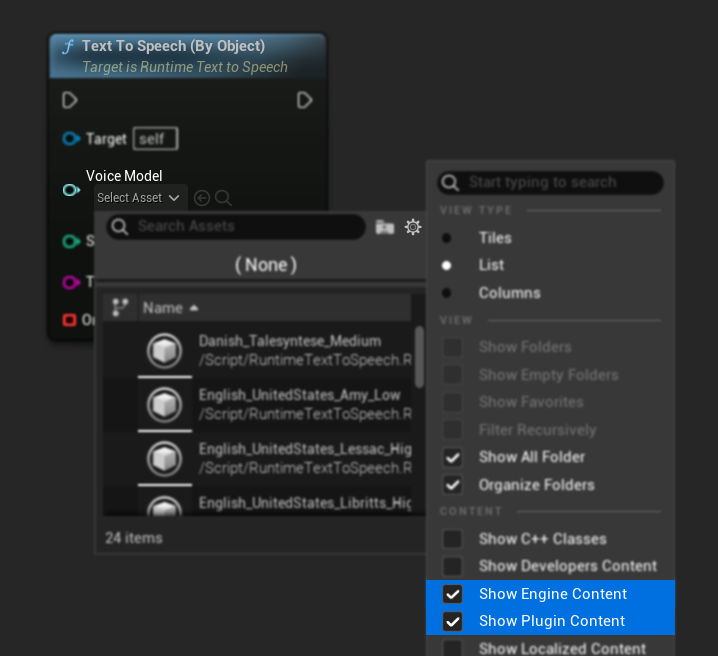
إذا قمت بتنزيل النماذج ولكن لا يمكنك رؤيتها، افتح القائمة المنسدلة Voice Model، انقر على الإعدادات (أيقونة الترس)، وقم بتمكين كل من Show Plugin Content و Show Engine Content لجعل النماذج مرئية.
في لغة C++، يمكن أن يكون اختيار نماذج الصوت أكثر تعقيدًا قليلاً بسبب عدم وجود قائمة منسدلة. يمكنك استخدام وظيفة GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames لاسترداد أسماء نماذج الصوت التي تم تنزيلها واختيار النموذج الذي تحتاجه. بعد ذلك، يمكنك استدعاء وظيفة GetVoiceModelFromName للحصول على كائن نموذج الصوت وتمريره إلى وظيفة TextToSpeechByObject لتركيب النص.
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
TSoftObjectPtr<URuntimeTTSModel> VoiceModel;
if (!URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetVoiceModelFromName(VoiceName, VoiceModel))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to get voice model from name: %s"), *VoiceName.ToString());
return;
}
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByObject(VoiceModel, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumChannels)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("TextToSpeech result: %s, AudioData size: %d, SampleRate: %d, NumChannels: %d"), bSuccess ? TEXT("Success") : TEXT("Failed"), AudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumChannels);
}));
return;
}
توليد الكلام من النص بالبث المباشر
للنصوص الطويلة أو عندما تريد معالجة بيانات الصوت في الوقت الفعلي أثناء إنشائها، يمكنك استخدام إصدارات البث المباشر لوظائف توليد الكلام من النص:
Streaming Text To Speech (By Name)(StreamingTextToSpeechByNameفي ++C)Streaming Text To Speech (By Object)(StreamingTextToSpeechByObjectفي ++C)
توفر هذه الوظائف بيانات الصوت على شكل أجزاء أثناء إنشائها، مما يسمح بالمعالجة الفورية دون الانتظار حتى اكتمال التوليد بالكامل. هذا مفيد لتطبيقات متنوعة مثل تشغيل الصوت في الوقت الفعلي، أو التصور الحي، أو أي سيناريو تحتاج فيه إلى معالجة بيانات الكلام بشكل تدريجي.
البث المباشر بالاسم
- Blueprint
- C++
تعمل وظيفة Streaming Text To Speech (By Name) بشكل مشابه للإصدار العادي ولكنها توفر الصوت على شكل أجزاء من خلال المفوض On Speech Chunk.
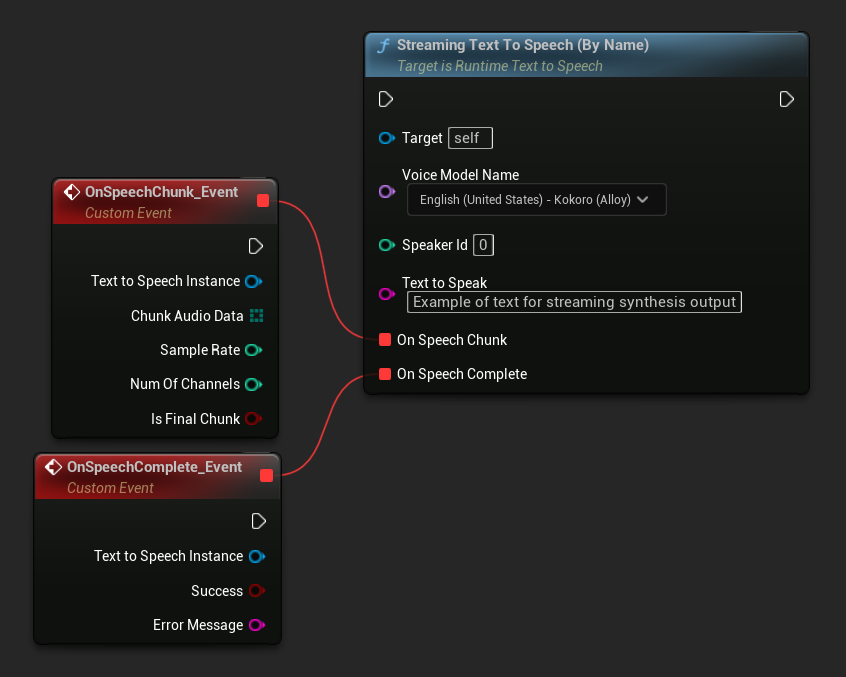
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByName(
VoiceName,
0,
TEXT("This is a long text that will be synthesized in chunks."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
// Process each chunk of audio data as it becomes available
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Received chunk %d with %d bytes of audio data. Sample rate: %d, Channels: %d, Is Final: %s"),
ChunkIndex, ChunkAudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumOfChannels, bIsFinalChunk ? TEXT("Yes") : TEXT("No"));
// You can start processing/playing this chunk immediately
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
// Called when the entire synthesis is complete or if it fails
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming synthesis completed successfully"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
البث حسب الكائن
- Blueprint
- C++
توفر وظيفة Streaming Text To Speech (By Object) نفس وظيفة البث ولكنها تأخذ مرجعًا لكائن نموذج صوتي.
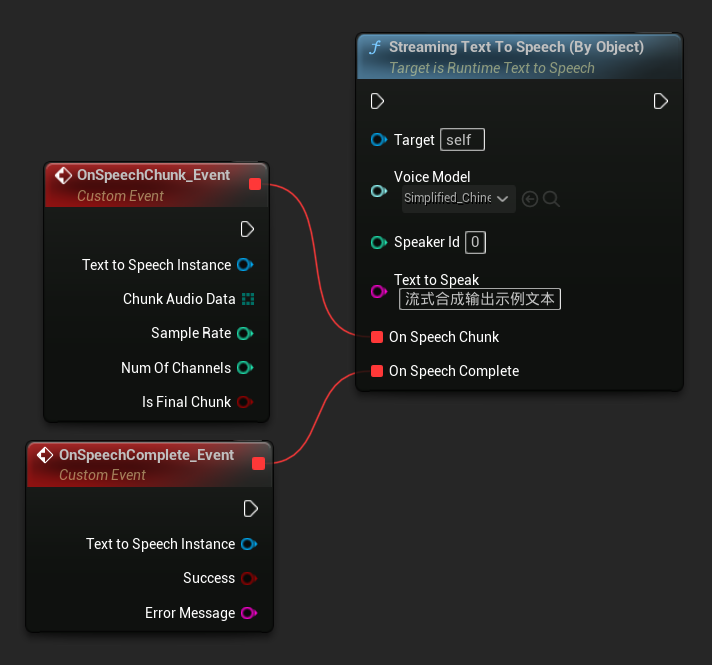
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
TSoftObjectPtr<URuntimeTTSModel> VoiceModel;
if (!URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetVoiceModelFromName(VoiceName, VoiceModel))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to get voice model from name: %s"), *VoiceName.ToString());
return;
}
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByObject(
VoiceModel,
0,
TEXT("This is a long text that will be synthesized in chunks."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
// Process each chunk of audio data as it becomes available
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Received chunk %d with %d bytes of audio data. Sample rate: %d, Channels: %d, Is Final: %s"),
ChunkIndex, ChunkAudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumOfChannels, bIsFinalChunk ? TEXT("Yes") : TEXT("No"));
// You can start processing/playing this chunk immediately
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
// Called when the entire synthesis is complete or if it fails
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming synthesis completed successfully"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
تشغيل الصوت
- التشغيل العادي
- تشغيل البث
بالنسبة لتحويل النص إلى كلام العادي (غير المتدفق)، فإن المفوض On Speech Result يوفر الصوت المُركب كبيانات PCM بتنسيق float (كمصفوفة بايت في Blueprints أو TArray<uint8> في C++)، بالإضافة إلى Sample Rate و Num Of Channels.
للتشغيل، يُوصى باستخدام ملحق Runtime Audio Importer لتحويل بيانات الصوت الخام إلى موجة صوتية قابلة للتشغيل.
- Blueprint
- C++
إليك مثالًا لكيفية ظهور عقد Blueprint لتركيب النص وتشغيل الصوت (عقد قابلة للنسخ):
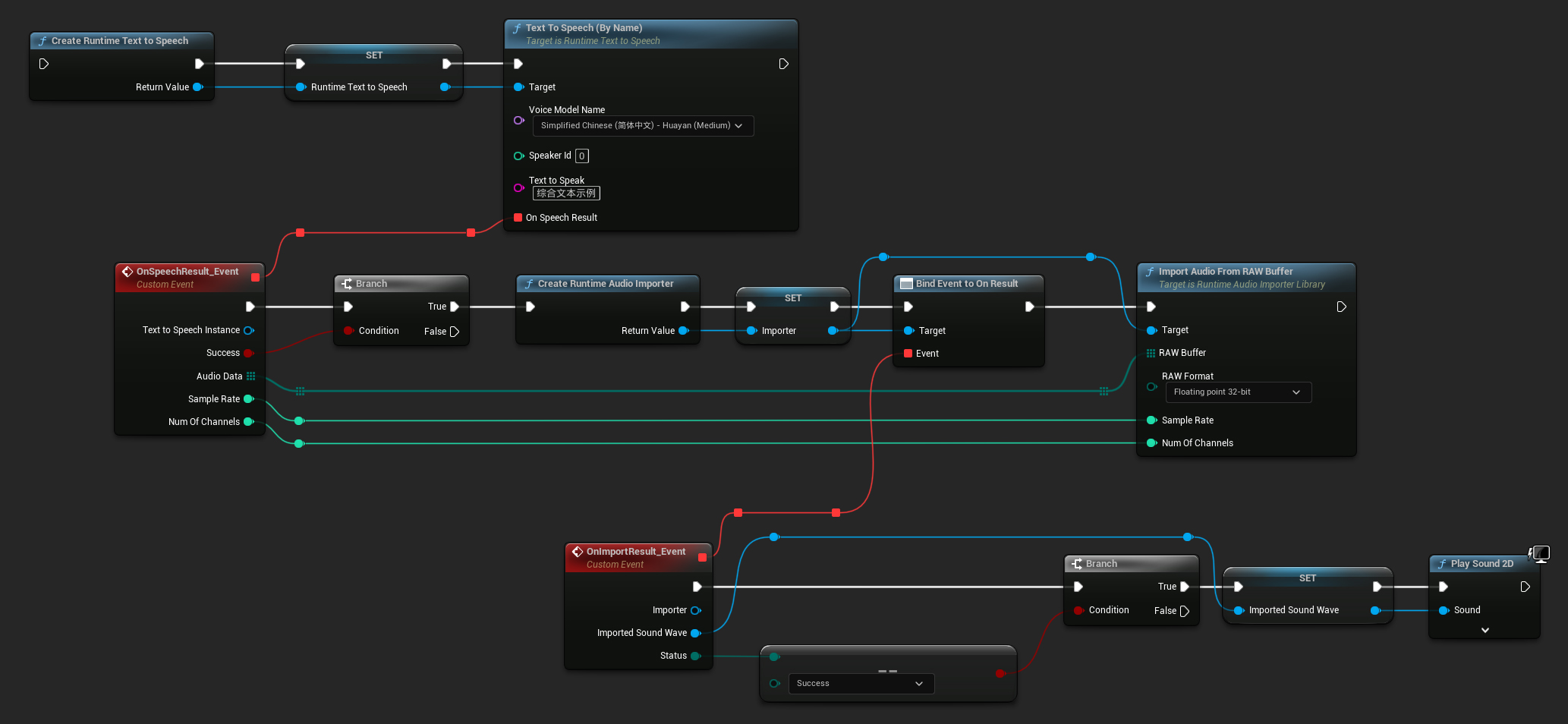
إليك مثالًا لكيفية تركيب النص وتشغيل الصوت في C++:
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
// Ensure "this" is a valid and referenced UObject (must not be eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels)
{
if (!bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("TextToSpeech failed"));
return;
}
// Create the Runtime Audio Importer to process the audio data
URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* RuntimeAudioImporter = URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary::CreateRuntimeAudioImporter();
// Prevent the RuntimeAudioImporter from being garbage collected by adding it to the root (you can also use a UPROPERTY, TStrongObjectPtr, etc.)
RuntimeAudioImporter->AddToRoot();
RuntimeAudioImporter->OnResultNative.AddWeakLambda(RuntimeAudioImporter, [this](URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* Importer, UImportedSoundWave* ImportedSoundWave, ERuntimeImportStatus Status)
{
// Once done, remove it from the root to allow garbage collection
Importer->RemoveFromRoot();
if (Status != ERuntimeImportStatus::SuccessfulImport)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to import audio, status: %s"), *UEnum::GetValueAsString(Status));
return;
}
// Play the imported sound wave (ensure a reference is kept to prevent garbage collection)
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), ImportedSoundWave);
});
RuntimeAudioImporter->ImportAudioFromRAWBuffer(AudioData, ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Float32, SampleRate, NumOfChannels);
}));
return;
}
للصوت النصي المُبَث، ستتلقى بيانات الصوت على شكل أجزاء كبيانات PCM بصيغة float (كمصفوفة بايت في Blueprints أو TArray<uint8> في C++)، جنبًا إلى جنب مع معدل العينة وعدد القنوات. يمكن معالجة كل جزء فور توفره.
للتشغيل في الوقت الفعلي، يُوصى باستخدام مكوّن Runtime Audio Importer الإضافي Streaming Sound Wave، المصمم خصيصًا لتشغيل الصوت المُبَث أو المعالجة في الوقت الفعلي.
- Blueprint
- C++
إليك مثالًا لكيفية ظهور عقد Blueprint للصوت النصي المُبَث وتشغيل الصوت (عقد قابلة للنسخ):
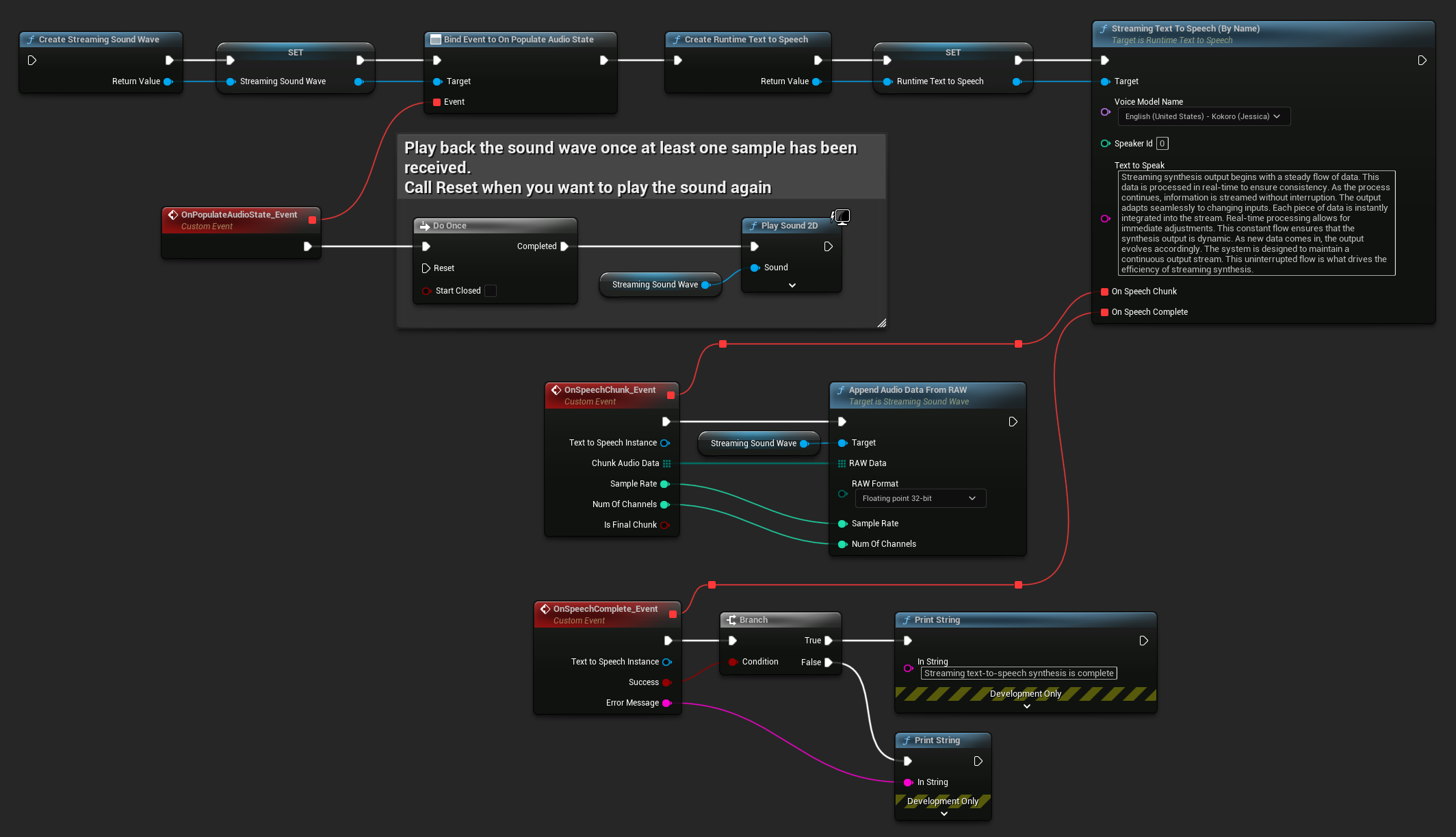
إليك مثالًا لكيفية تنفيذ الصوت النصي المُبَث مع التشغيل في الوقت الفعلي في C++:
UPROPERTY()
URuntimeTextToSpeech* Synthesizer;
UPROPERTY()
UStreamingSoundWave* StreamingSoundWave;
UPROPERTY()
bool bIsPlaying = false;
void StartStreamingTTS()
{
// Create synthesizer if not already created
if (!Synthesizer)
{
Synthesizer = URuntimeTextToSpeech::CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech();
}
// Create a sound wave for streaming if not already created
if (!StreamingSoundWave)
{
StreamingSoundWave = UStreamingSoundWave::CreateStreamingSoundWave();
StreamingSoundWave->OnPopulateAudioStateNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [this]()
{
if (!bIsPlaying)
{
bIsPlaying = true;
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), StreamingSoundWave);
}
});
}
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByName(
VoiceName,
0,
TEXT("Streaming synthesis output begins with a steady flow of data. This data is processed in real-time to ensure consistency. As the process continues, information is streamed without interruption. The output adapts seamlessly to changing inputs. Each piece of data is instantly integrated into the stream. Real-time processing allows for immediate adjustments. This constant flow ensures that the synthesis output is dynamic. As new data comes in, the output evolves accordingly. The system is designed to maintain a continuous output stream. This uninterrupted flow is what drives the efficiency of streaming synthesis."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
StreamingSoundWave->AppendAudioDataFromRAW(ChunkAudioData, ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Float32, SampleRate, NumOfChannels);
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming text-to-speech synthesis is complete"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
}
إلغاء تحويل النص إلى كلام
يمكنك إلغاء عملية تحويل النص إلى كلام الجارية في أي وقت عن طريق استدعاء الدالة CancelSpeechSynthesis على مثيل المترجم الخاص بك:
- Blueprint
- C++
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid URuntimeTextToSpeech instance
// Start a long synthesis operation
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Very long text..."), ...);
// Later, if you need to cancel it:
bool bWasCancelled = Synthesizer->CancelSpeechSynthesis();
if (bWasCancelled)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Successfully cancelled ongoing synthesis"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("No synthesis was in progress to cancel"));
}
عند إلغاء عملية التوليف:
- ستتوقف عملية التوليف في أسرع وقت ممكن
- سيتم إنهاء أي استدعاءات جارية (callbacks)
- سيتم استدعاء مندوب الإكمال (completion delegate) مع
bSuccess = falseورسالة خطأ تشير إلى أنه تم إلغاء التوليف - سيتم تنظيف أي موارد مخصصة للتوليف بشكل صحيح
هذا مفيد بشكل خاص للنصوص الطويلة أو عندما تحتاج إلى مقاطعة التشغيل لبدء توليف جديد.
اختيار المتحدث (Speaker Selection)
تقبل وظيفتا Text To Speech معاملًا اختياريًا لمعرّف المتحدث (speaker ID)، وهو مفيد عند العمل مع نماذج الأصوات التي تدعم متحدثين متعددين. يمكنك استخدام وظائف GetSpeakerCountFromVoiceModel أو GetSpeakerCountFromModelName للتحقق مما إذا كان نموذج الصوت المختار يدعم متحدثين متعددين. إذا كانت هناك متحدثون متعددون متاحون، ما عليك سوى تحديد معرّف المتحدث المطلوب عند استدعاء وظائف Text To Speech. تقدم بعض نماذج الأصوات تنوعًا واسعًا - على سبيل المثال، English LibriTTS يتضمن أكثر من 900 متحدث مختلف للاختيار من بينهم.
تقدم إضافة Runtime Audio Importer أيضًا ميزات إضافية مثل تصدير بيانات الصوت إلى ملف، أو تمريرها إلى SoundCue، وMetaSound، والمزيد. لمزيد من التفاصيل، راجع وثائق Runtime Audio Importer.