プラグインの使用方法
Runtime Text To Speech プラグインは、ダウンロード可能な音声モデルを使用してテキストを音声に合成します。これらのモデルは、エディタ内のプラグイン設定で管理され、ダウンロードされ、ランタイム使用のためにパッケージ化されます。以下の手順に従って開始してください。
エディタ側
こちらで説明されているように、プロジェクトに適した音声モデルをダウンロードしてください。複数の音声モデルを同時にダウンロードすることができます。
ランタイム側
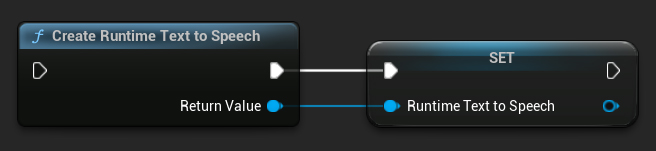
CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech 関数を使用してシンセサイザーを作成します。ガベージコレクションによって破棄されないように、その参照を維持することを確認してください(例:Blueprints では別の変数として、C++ では UPROPERTY として)。
- Blueprint
- C++
// Create the Runtime Text To Speech synthesizer in C++
URuntimeTextToSpeech* Synthesizer = URuntimeTextToSpeech::CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech();
// Ensure the synthesizer is referenced correctly to prevent garbage collection (e.g. as a UPROPERTY)
音声合成
このプラグインは2つのテキスト読み上げ合成モードを提供します:
- 通常のテキスト読み上げ: テキスト全体を合成し、完了時に完全なオーディオを返します
- ストリーミングテキスト読み上げ: 生成されたオーディオチャンクをリアルタイムで提供し、リアルタイム処理を可能にします
各モードは音声モデルを選択するための2つの方法をサポートしています:
- 名前による選択: 音声モデルを名前で選択します(UE 5.4+で推奨)
- オブジェクトによる選択: 音声モデルを直接参照で選択します(UE 5.3以前で推奨)
通常のテキスト読み上げ
名前による選択
- Blueprint
- C++
Text To Speech (By Name) 関数は、UE 5.4 以降の Blueprints でより便利です。ダウンロードされたモデルのドロップダウンリストから音声モデルを選択できます。UE 5.3 以下のバージョンでは、このドロップダウンは表示されないため、古いバージョンを使用している場合は、GetDownloadedVoiceModels によって返される音声モデルの配列を手動で反復処理して、必要なモデルを選択する必要があります。
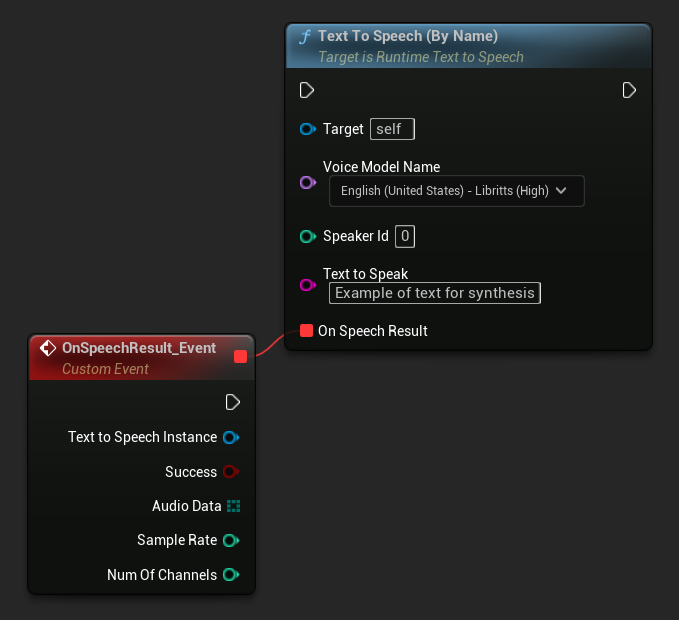
C++では、ドロップダウンリストがないため、音声モデルの選択が少し複雑になる場合があります。GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames 関数を使用して、ダウンロードされた音声モデルの名前を取得し、必要なモデルを選択できます。その後、TextToSpeechByName 関数を呼び出して、選択した音声モデル名を使用してテキストを合成できます。
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, just as an example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumChannels)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("TextToSpeech result: %s, AudioData size: %d, SampleRate: %d, NumChannels: %d"), bSuccess ? TEXT("Success") : TEXT("Failed"), AudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumChannels);
}));
return;
}
オブジェクト指定
- Blueprint
- C++
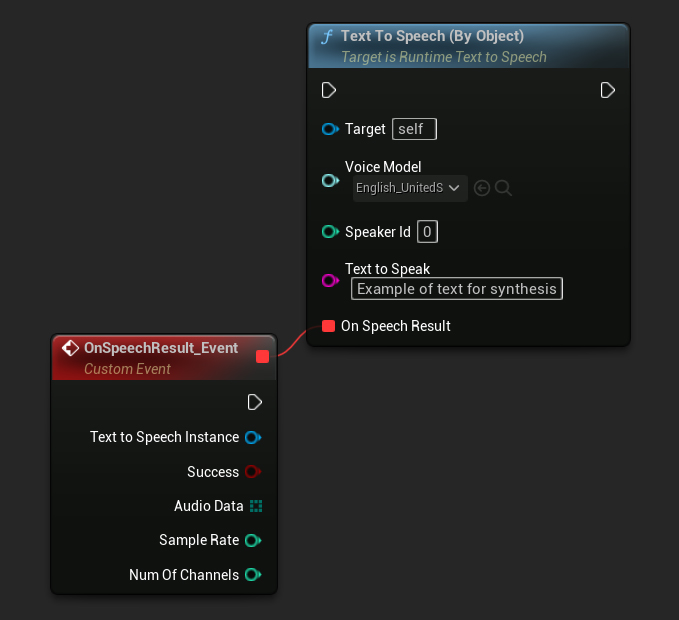
Text To Speech (By Object) 関数は Unreal Engine の全バージョンで動作しますが、音声モデルをアセット参照のドロップダウンリストとして表示するため、直感的ではありません。この方法は UE 5.3 以前、または何らかの理由でプロジェクトが音声モデルアセットへの直接参照を必要とする場合に適しています。
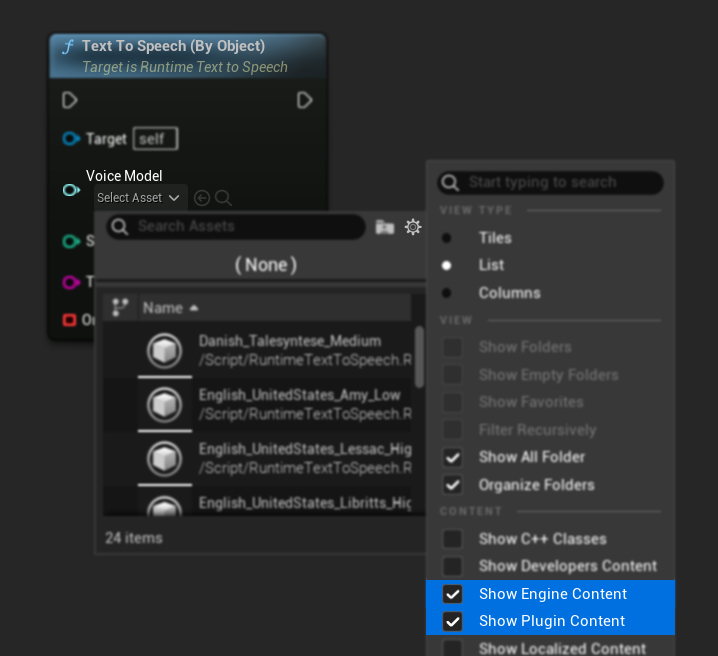
モデルをダウンロードしたのに表示されない場合は、Voice Model ドロップダウンを開き、設定(歯車アイコン)をクリックして、Show Plugin Content と Show Engine Content の両方を有効にするとモデルが表示されます。
C++ では、ドロップダウンリストがないため、音声モデルの選択が少し複雑になる場合があります。ダウンロードされた音声モデルの名前を取得するには GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames 関数を使用し、必要なモデルを選択できます。その後、GetVoiceModelFromName 関数を使用して音声モデルオブジェクトを取得し、それを TextToSpeechByObject 関数に渡してテキストを合成できます。
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
TSoftObjectPtr<URuntimeTTSModel> VoiceModel;
if (!URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetVoiceModelFromName(VoiceName, VoiceModel))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to get voice model from name: %s"), *VoiceName.ToString());
return;
}
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByObject(VoiceModel, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumChannels)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("TextToSpeech result: %s, AudioData size: %d, SampleRate: %d, NumChannels: %d"), bSuccess ? TEXT("Success") : TEXT("Failed"), AudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumChannels);
}));
return;
}
ストリーミング テキスト読み上げ
長いテキストの場合や、生成されたオーディオデータをリアルタイムで処理したい場合には、ストリーミング版の Text-to-Speech 関数を使用できます:
Streaming Text To Speech (By Name)(C++ ではStreamingTextToSpeechByName)Streaming Text To Speech (By Object)(C++ ではStreamingTextToSpeechByObject)
これらの関数は、生成される際にオーディオデータをチャンク単位で提供するため、合成全体が完了するのを待たずに即座に処理を行うことができます。これは、リアルタイムのオーディオ再生、ライブでの可視化、または音声データを段階的に処理する必要があるあらゆるシナリオで有用です。
名前によるストリーミング
- Blueprint
- C++
Streaming Text To Speech (By Name) 関数は通常版と同様に動作しますが、On Speech Chunk デリゲートを通じてオーディオをチャンク単位で提供します。
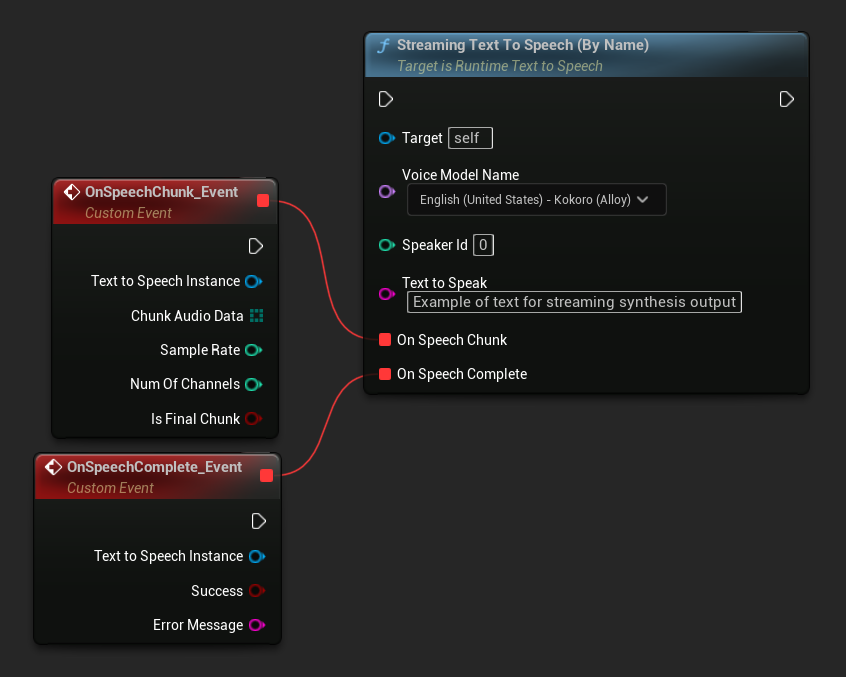
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByName(
VoiceName,
0,
TEXT("This is a long text that will be synthesized in chunks."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
// Process each chunk of audio data as it becomes available
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Received chunk %d with %d bytes of audio data. Sample rate: %d, Channels: %d, Is Final: %s"),
ChunkIndex, ChunkAudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumOfChannels, bIsFinalChunk ? TEXT("Yes") : TEXT("No"));
// You can start processing/playing this chunk immediately
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
// Called when the entire synthesis is complete or if it fails
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming synthesis completed successfully"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
オブジェクトによるストリーミング
- Blueprint
- C++
Streaming Text To Speech (By Object) 関数は同じストリーミング機能を提供しますが、ボイスモデルのオブジェクト参照を受け取ります。
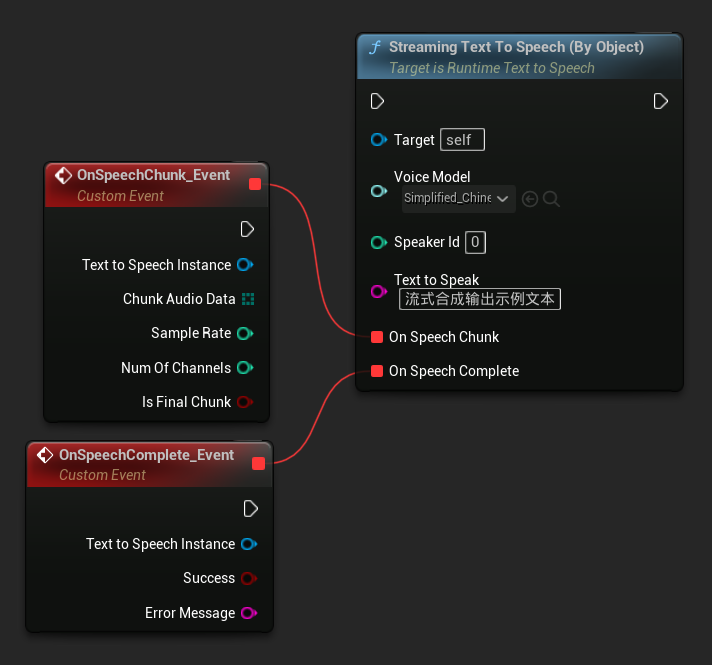
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
TSoftObjectPtr<URuntimeTTSModel> VoiceModel;
if (!URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetVoiceModelFromName(VoiceName, VoiceModel))
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to get voice model from name: %s"), *VoiceName.ToString());
return;
}
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByObject(
VoiceModel,
0,
TEXT("This is a long text that will be synthesized in chunks."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
// Process each chunk of audio data as it becomes available
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Received chunk %d with %d bytes of audio data. Sample rate: %d, Channels: %d, Is Final: %s"),
ChunkIndex, ChunkAudioData.Num(), SampleRate, NumOfChannels, bIsFinalChunk ? TEXT("Yes") : TEXT("No"));
// You can start processing/playing this chunk immediately
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateLambda([](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
// Called when the entire synthesis is complete or if it fails
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming synthesis completed successfully"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
オーディオ再生
- 通常再生
- ストリーミング再生
通常の(ストリーミングではない)テキスト読み上げの場合、On Speech Result デリゲートは、合成されたオーディオを PCM データ(float 形式、Blueprints ではバイト配列、C++ では TArray<uint8> として)と、Sample Rate および Num Of Channels を提供します。
再生には、Runtime Audio Importer プラグインを使用して生のオーディオデータを再生可能なサウンドウェーブに変換することを推奨します。
- Blueprint
- C++
以下は、テキストを合成しオーディオを再生する Blueprint ノードの例です(コピー可能なノード):
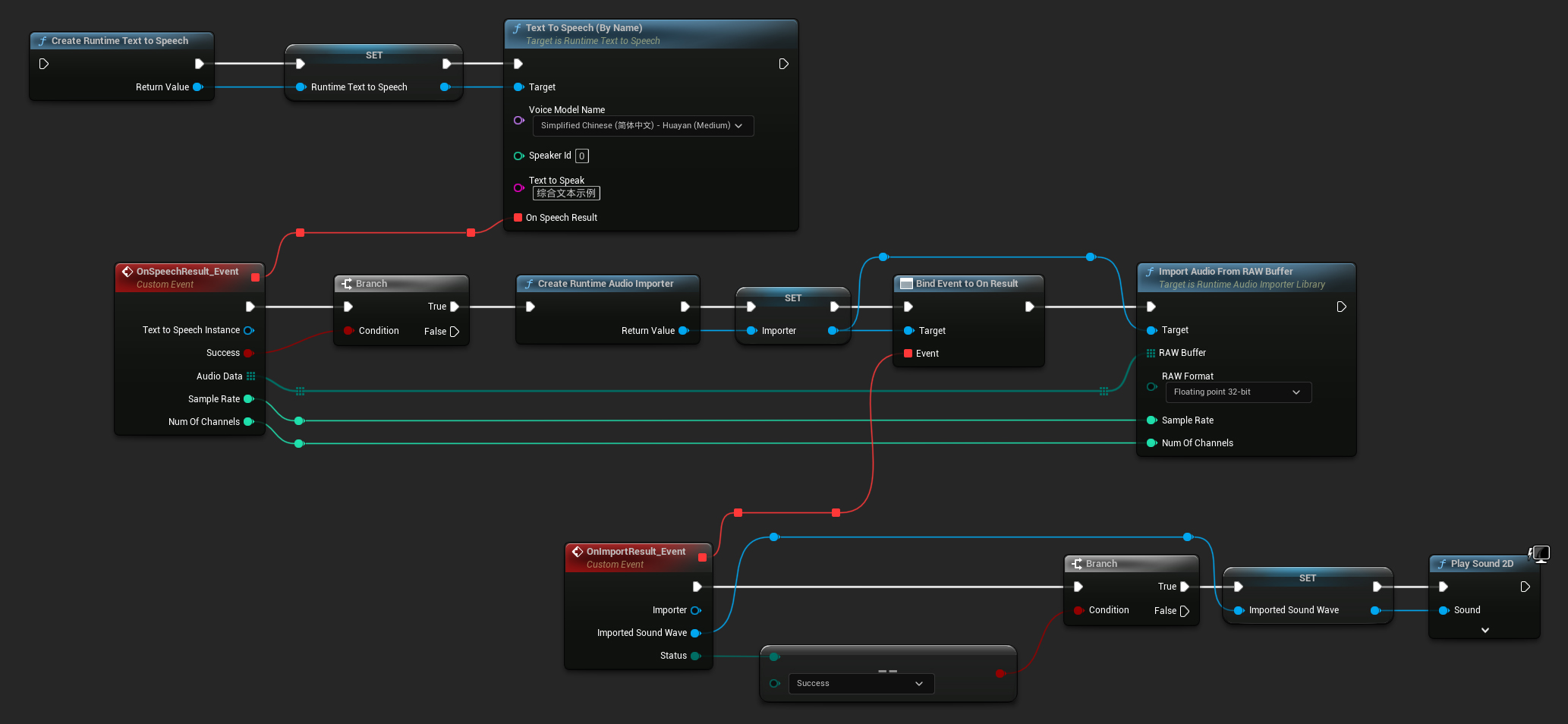
以下は、C++ でテキストを合成しオーディオを再生する方法の例です:
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid and referenced URuntimeTextToSpeech object (ensure it is not eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
// Ensure "this" is a valid and referenced UObject (must not be eligible for garbage collection during the callback)
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Text example 123"), FOnTTSResultDelegateFast::CreateLambda([this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const TArray<uint8>& AudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels)
{
if (!bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("TextToSpeech failed"));
return;
}
// Create the Runtime Audio Importer to process the audio data
URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* RuntimeAudioImporter = URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary::CreateRuntimeAudioImporter();
// Prevent the RuntimeAudioImporter from being garbage collected by adding it to the root (you can also use a UPROPERTY, TStrongObjectPtr, etc.)
RuntimeAudioImporter->AddToRoot();
RuntimeAudioImporter->OnResultNative.AddWeakLambda(RuntimeAudioImporter, [this](URuntimeAudioImporterLibrary* Importer, UImportedSoundWave* ImportedSoundWave, ERuntimeImportStatus Status)
{
// Once done, remove it from the root to allow garbage collection
Importer->RemoveFromRoot();
if (Status != ERuntimeImportStatus::SuccessfulImport)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Failed to import audio, status: %s"), *UEnum::GetValueAsString(Status));
return;
}
// Play the imported sound wave (ensure a reference is kept to prevent garbage collection)
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), ImportedSoundWave);
});
RuntimeAudioImporter->ImportAudioFromRAWBuffer(AudioData, ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Float32, SampleRate, NumOfChannels);
}));
return;
}
ストリーミング音声合成では、PCMデータ(float形式、Blueprintsではバイト配列、C++ではTArray<uint8>として)がチャンク単位で、Sample Rate(サンプルレート)およびNum Of Channels(チャンネル数)と共に送信されます。各チャンクは利用可能になり次第、即座に処理することができます。
リアルタイム再生には、ストリーミングオーディオ再生やリアルタイム処理に特化して設計されたRuntime Audio ImporterプラグインのStreaming Sound Waveの使用を推奨します。
- Blueprint
- C++
以下は、ストリーミング音声合成とオーディオ再生のためのBlueprintノードの例です(コピー可能なノード):
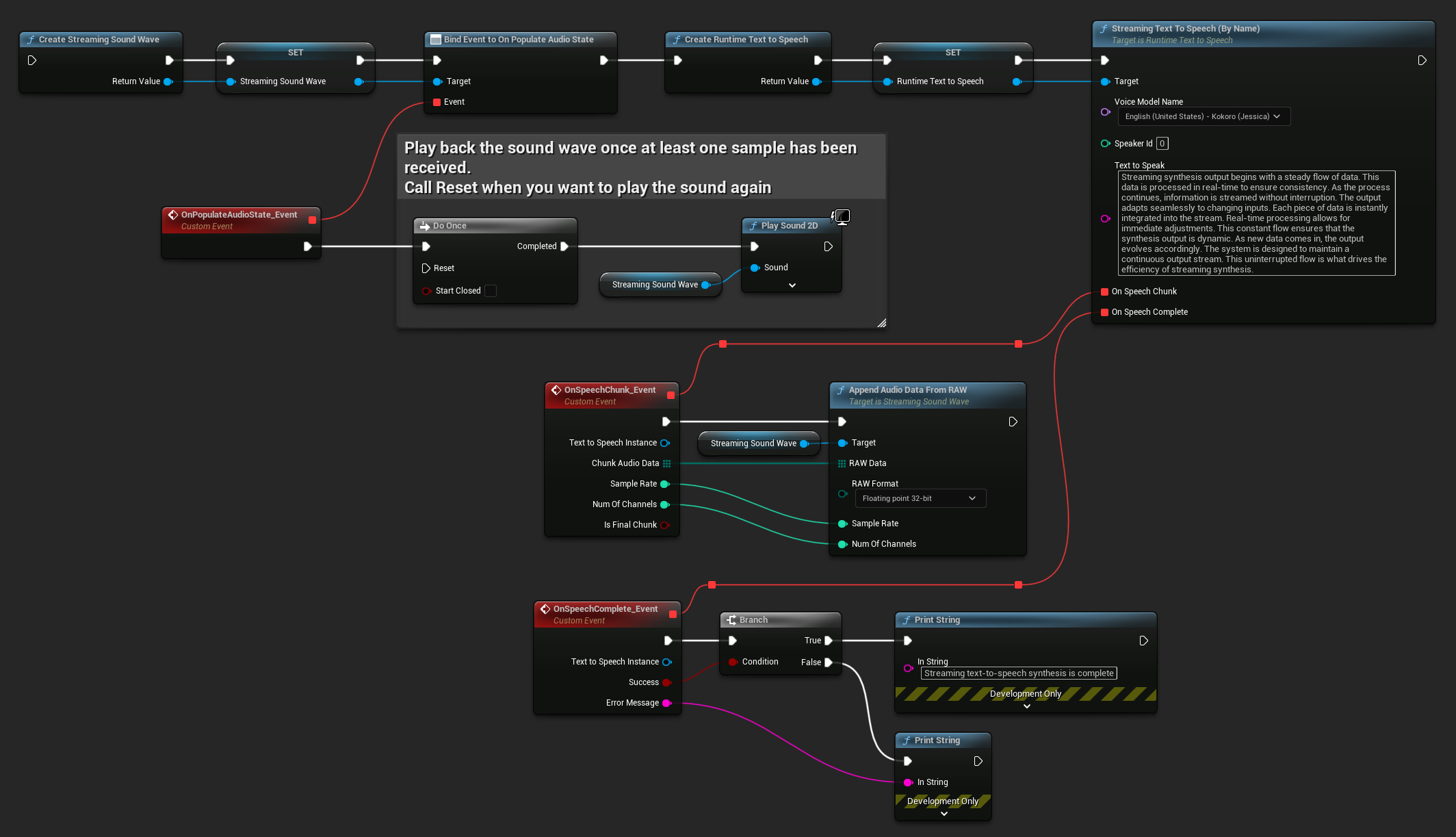
以下は、C++でストリーミング音声合成をリアルタイム再生と共に実装する方法の例です:
UPROPERTY()
URuntimeTextToSpeech* Synthesizer;
UPROPERTY()
UStreamingSoundWave* StreamingSoundWave;
UPROPERTY()
bool bIsPlaying = false;
void StartStreamingTTS()
{
// Create synthesizer if not already created
if (!Synthesizer)
{
Synthesizer = URuntimeTextToSpeech::CreateRuntimeTextToSpeech();
}
// Create a sound wave for streaming if not already created
if (!StreamingSoundWave)
{
StreamingSoundWave = UStreamingSoundWave::CreateStreamingSoundWave();
StreamingSoundWave->OnPopulateAudioStateNative.AddWeakLambda(this, [this]()
{
if (!bIsPlaying)
{
bIsPlaying = true;
UGameplayStatics::PlaySound2D(GetWorld(), StreamingSoundWave);
}
});
}
TArray<FName> DownloadedVoiceNames = URuntimeTTSLibrary::GetDownloadedVoiceModelNames();
// If there are downloaded voice models, use the first one to synthesize text, for example
if (DownloadedVoiceNames.Num() > 0)
{
const FName& VoiceName = DownloadedVoiceNames[0]; // Select the first available voice model
Synthesizer->StreamingTextToSpeechByName(
VoiceName,
0,
TEXT("Streaming synthesis output begins with a steady flow of data. This data is processed in real-time to ensure consistency. As the process continues, information is streamed without interruption. The output adapts seamlessly to changing inputs. Each piece of data is instantly integrated into the stream. Real-time processing allows for immediate adjustments. This constant flow ensures that the synthesis output is dynamic. As new data comes in, the output evolves accordingly. The system is designed to maintain a continuous output stream. This uninterrupted flow is what drives the efficiency of streaming synthesis."),
FOnTTSStreamingChunkDelegateFast::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, const TArray<uint8>& ChunkAudioData, int32 SampleRate, int32 NumOfChannels, bool bIsFinalChunk)
{
StreamingSoundWave->AppendAudioDataFromRAW(ChunkAudioData, ERuntimeRAWAudioFormat::Float32, SampleRate, NumOfChannels);
}),
FOnTTSStreamingCompleteDelegateFast::CreateWeakLambda(this, [this](URuntimeTextToSpeech* TextToSpeechInstance, bool bSuccess, const FString& ErrorMessage)
{
if (bSuccess)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Streaming text-to-speech synthesis is complete"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("Streaming synthesis failed: %s"), *ErrorMessage);
}
})
);
}
}
テキスト読み上げのキャンセル
進行中のテキスト読み上げ合成操作は、いつでもシンセサイザーインスタンスの CancelSpeechSynthesis 関数を呼び出すことでキャンセルできます:
- Blueprint
- C++
// Assuming "Synthesizer" is a valid URuntimeTextToSpeech instance
// Start a long synthesis operation
Synthesizer->TextToSpeechByName(VoiceName, 0, TEXT("Very long text..."), ...);
// Later, if you need to cancel it:
bool bWasCancelled = Synthesizer->CancelSpeechSynthesis();
if (bWasCancelled)
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("Successfully cancelled ongoing synthesis"));
}
else
{
UE_LOG(LogTemp, Log, TEXT("No synthesis was in progress to cancel"));
}
音声合成がキャンセルされた場合:
- 音声合成プロセスは可能な限り速やかに停止します
- 進行中のコールバックは終了されます
- 完了デリゲートは
bSuccess = falseと、合成がキャンセルされたことを示すエラーメッセージを伴って呼び出されます - 合成のために割り当てられたリソースは適切にクリーンアップされます
これは長文テキストの場合や、新しい合成を開始するために再生を中断する必要がある場合に特に便利です。
スピーカー選択
両方の Text To Speech 関数は、オプションのスピーカーIDパラメータを受け入れます。これは複数のスピーカーをサポートする音声モデルを使用する場合に便利です。選択した音声モデルが複数のスピーカーをサポートしているかどうかを確認するには、GetSpeakerCountFromVoiceModel または GetSpeakerCountFromModelName 関数を使用できます。複数のスピーカーが利用可能な場合、Text To Speech 関数を呼び出す際に希望するスピーカーIDを指定するだけです。一部の音声モデルは広範なバラエティを提供します - 例えば、English LibriTTS には900人以上の異なるスピーカーから選択できます。
Runtime Audio Importer プラグインは、オーディオデータをファイルにエクスポートしたり、SoundCueやMetaSoundなどに渡すといった追加機能も提供します。詳細については、Runtime Audio Importer ドキュメントを確認してください。